Figure 2. Accumulation capacity and trapping efficacy of surface-attached micro-traps.
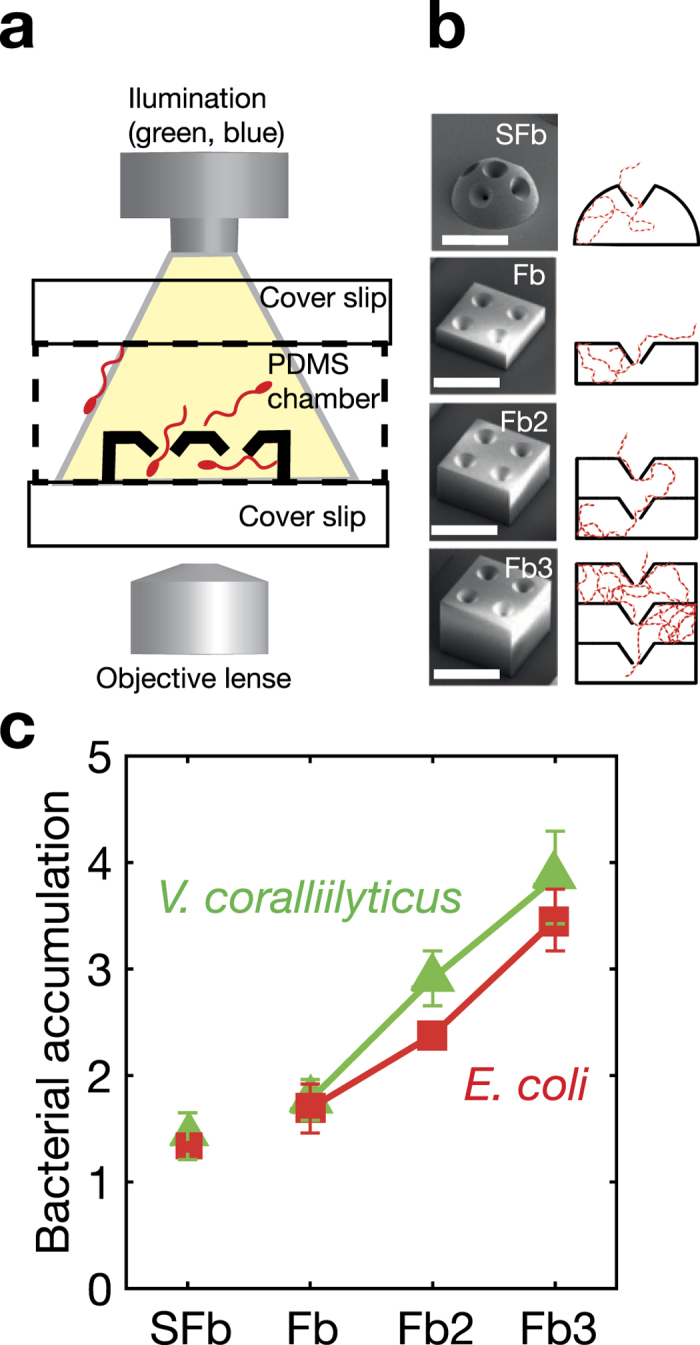
(a) Structures are attached on a cover glass with a PDMS gasket under an inverted fluorescent microscope. (b) SEM images (left-hand side) and cross-sections (right-hand side) of dome-shaped (SFb) and multilayer squared micro-structures (Fb1, Fb2, and Fb3). Scale bar, 100 μm. Squared micro structure having a size of 150 μm × 150 μm × 50 μm and 4 funnel apertures having an external diameter of 45 μm and an internal diameter of 10 μm (Fb). The height of the apertures in z-direction is 25 μm. Structures with 1, 2 (Fb2) and 3 (Fb3) stacked squared microstructure. The distance between two sequential apertures in z-direction is 25 μm. Dome-shaped micro structure (SFb) having a diameter of 150 μm and 5 funnel apertures with an external diameter of 45 μm and an internal diameter of 10 μm. The wall thickness of all structures is 8 μm. Red dashed lines: Simulated trajectories of a single bacterium swimming in different cross sections. (c) Bacterial accumulation for different surface-attached micro-traps and for two bacterial species after about 3 hours: E. coli (Red squares) V. coralliilyticus (green squares). Error bars correspond to the standard error of the mean for at least 3 independent experiments.
