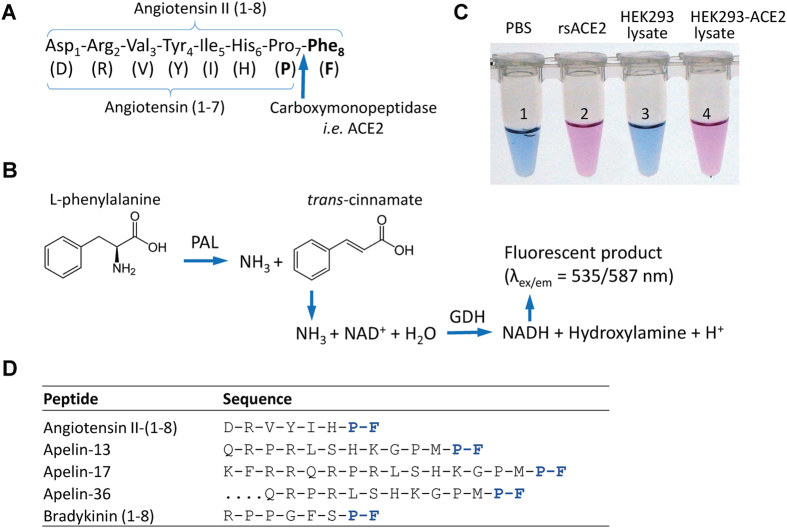
Figure 1. Schematics of the Ang II phenylalanine assay.
(A) The assay measures the rate of Ang II cleavage at the peptide bond of proline7-phenylalanine8 by ACE2 or other equivalent carboxymonopeptidases (arrow). (B) Following the proteolytic cleavage, the amino group of phenylalanine becomes exposed to undergo deamidation by yeast enzyme phenylalanine ammonia lyase (PAL), also termed phenylalanine deaminase. Following a series of coupled reactions, a fluorogenic substrate is converted, and the rate of conversion that reflects the kinetic of the first reaction can be quantitatively measured. (C) The picture shows the color change as the result of the chain of the reaction initiated by ACE2 cleavage of synthetic Ang II peptide. Tubes 1 and 2 are from reactions in the absence and presence of recombinant soluble ACE2 (rsACE2: aa 1–740), respectively; tubes 3 and 4 are each from reactions with the addition of culture medium from cells transfected with either pcDNA3 empty vector or a soluble ACE2-expressing plasmid respectively. Positive ACE2 enzymatic activities in 2 and 4 convert fluorogenic substrate to bright pink color visible to naked eyes (with emission at 587 nm). (D) Several bioactive peptides share the same proline-phenylalanine (P-F) motif at their C-termini.