Fig. 3.
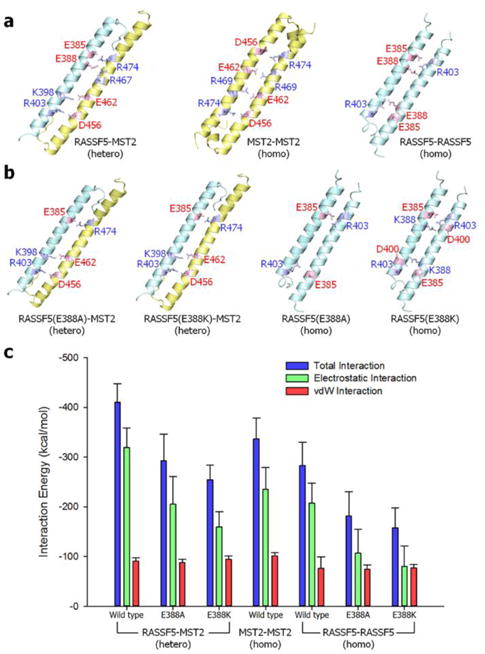
The SARAH-SARAH interaction in the coiled coil dimer. (a) Averaged structures of RASSF5-MST2 SARAH heterodimer (left), MST2-MST2 (center) and RASSF5-RASSF5 (right) homodimers. (b) Averaged structures of RASSF5-MST2 SARAH heterodimers with the E388A (far left) and E388K (second left) mutations in RASSF5, and RASSF5-RASSF5 SARAH homodimers with the E388A (second right) and E388K (far right) mutations in RASSF5. In the ribbon representation, RASSF5 and MST2 are colored cyan and yellow, respectively. The salt bridge pairs are shown in the average structures of each SARAH-SARAH dimer. (c) Interaction energy gauging the SARAH-SARAH association in the coiled coil dimer. Averaged total interaction energy (blue bars), and the contributions from the electrostatic (green bars) and vdW (red bars) interactions for three different SARAH dimers are shown.
