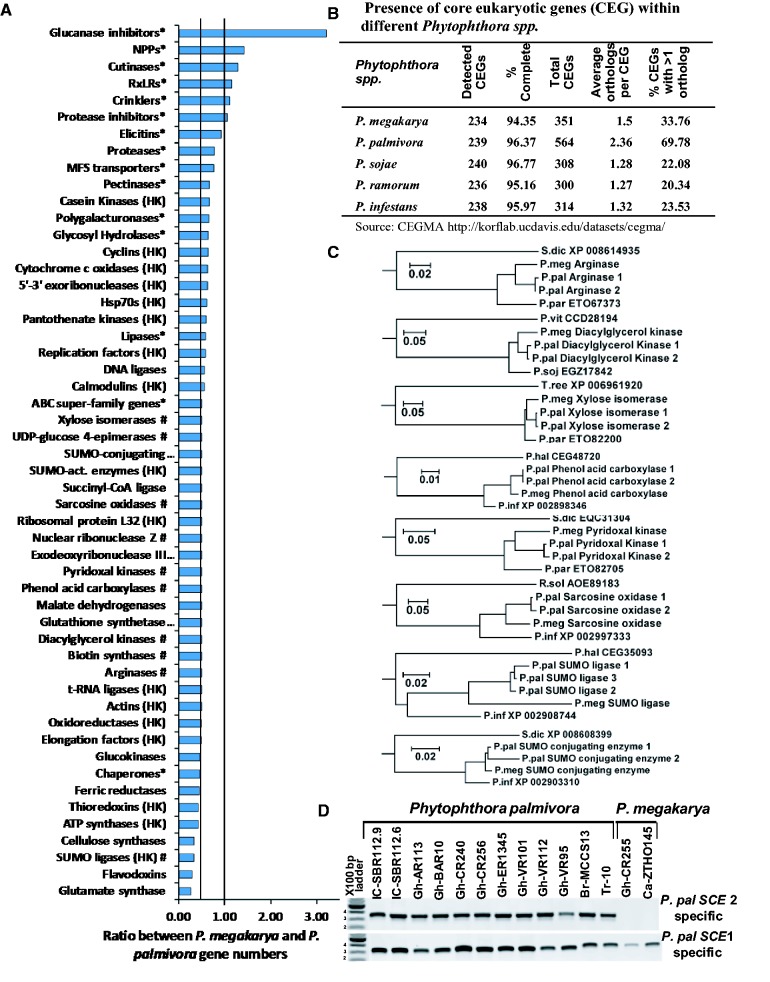
Fig. 1.—
Comparison of the gene complements of P. megakarya and P. palmivora. (A) The ratio between gene model numbers of selected P. megakarya and P. palmivora gene families. (HK housekeeping gene; # gene families with a single-copy gene model in P. megakarya; * gene families related to plant-infection). (B) Presence of CEGs within different Phytophthora spp. based on the CEGMA output report (Parra et al. 2007). (C) Evolutionary relationship between eight randomly selected gene models where there is only a single copy in P. megakarya but there are two homeologous copies in P. palmivora. Amino acid sequence similarities were inferred using guide trees generated by WebPRANK (http://www.ebi.ac.uk/goldman-srv/webprank/, last accessed 16 February 2017). Branch length represents the number of amino acid substitutions per site. (S.dic, Saprolegnia diclina; P.meg, P. megakarya; P.pal, P. palmivora; P.par, P. parasitica; P.vit, Plasmopara viticola; P.soj, P. sojae; T.ree, Trichoderma reesei; P.inf, P. infestans; R.sol, Ralstonia solanacearum; P.hal, Plasmopara halstedii). (D) PCR amplification of SCE with two P. palmivora homeolog-specific PCR primer sets across 12 P. palmivora and 2 P. megakarya isolates (Ali et al. 2016).