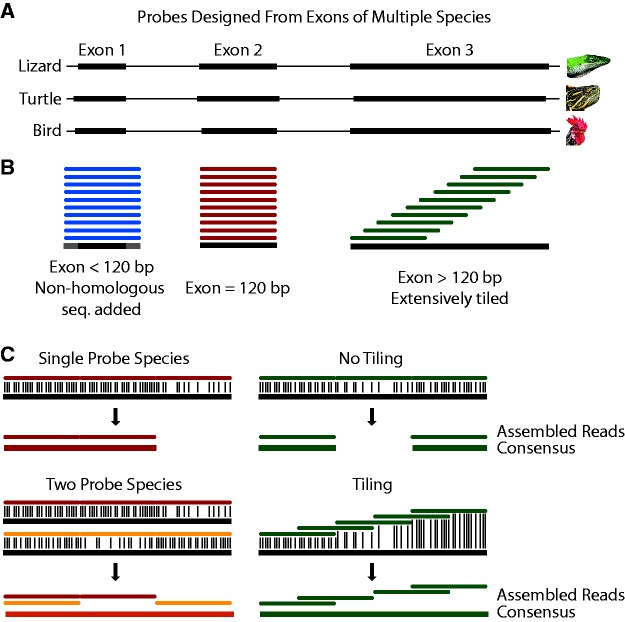
Fig. 1.—
Cross-species hybrid capture methods. (A), exons were extracted from the genomes of an average of three reference species (anole, turtle, and chicken). (B), probes were designed against each exon. Since probe length was constant at 120 bp, exons shorter than the probe length were padded with non-homologous sequence. Exons the same length as the probe matched exactly, while those longer were extensively tiled across the exon (10X coverage). The overall number of probes covering each base was normalized to ensure even coverage. (C), multiple reference species and tiling were designed to help facilitate cross-species capture. For example, a region of high divergence may occur in one species and not another, or could still be captured by tiling across it.