Fig. 1.—
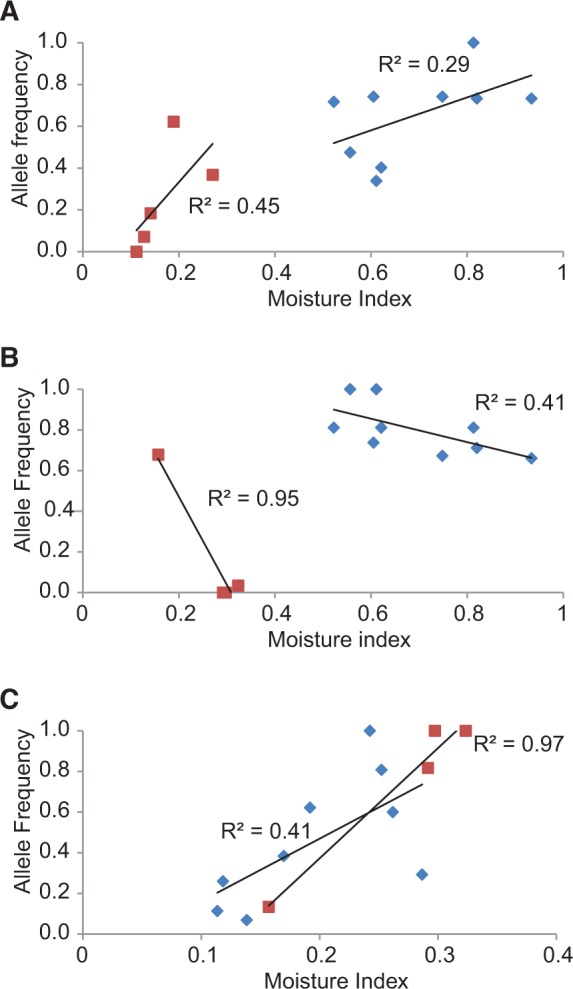
Linear regression of population-level allele frequencies of outlier markers that were common to two of the three studied Eucalyptus species plotted against a moisture index (“Aridity Index” from the Atlas of Living Australia = precipitation/pan evaporation). The markers were also correlated with other environmental variables (supplementary material S2, Supplementary Material online). (A) TriDArTseq 1174 (E. tricarpa, blue diamond) and SalDArTseq 9159 (E. salubris lineage 1, brown square) were both In Eucgr.A02872 (Chromosome 1), K13458—a disease resistance gene; (B) TriDArTseq 1079 (E. tricarpa, blue diamond) and SalDArTseq 3803 (E. salubris lineage 2, brown square) were both In Eucgr.F00208 (Chromosome 6), a proprotein convertase subtilisin/kexin gene; (C) LoxDArTseq 1012 (E. loxophleba, blue diamond) and SalDArTseq 11926 (E. salubris lineage 2, brown square) were both Near Eucgr.G00352 (Chromosome 7), an ATP phosphoribosyl-transferase gene. See text for definitions of In versus Near genes.
