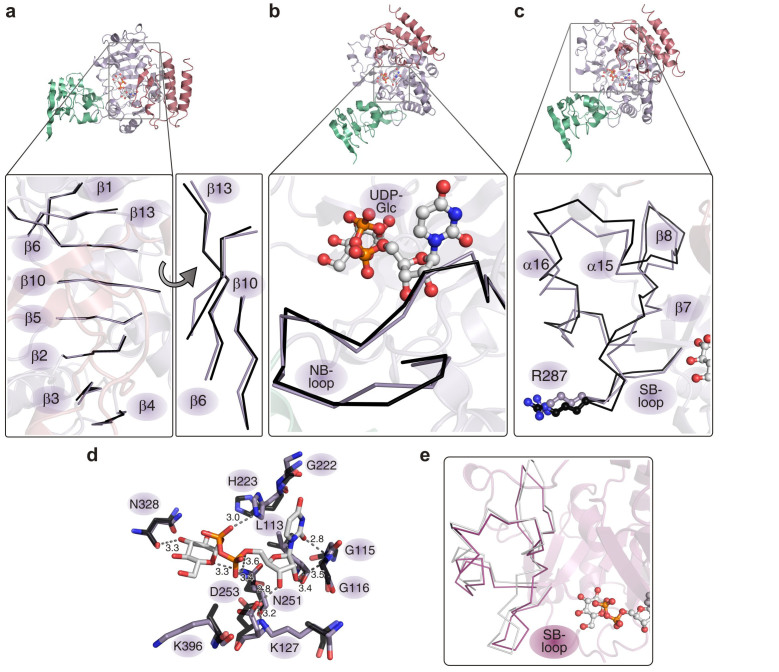
Figure 3. Superposition of hUGP active site elements in apo- (PDB ID: 2R2W; black) and UDP-Glc bound states (this study; purple).
(a) The eight-stranded β-sheet, forming the active site cleft (left panel) undergoes a torsional deformation (right panel) upon UDP-Glc binding with maximum displacement of 1.4 Å for the Cα atoms and 3.4 Å for the side chains. (b) Coordination of UDP-Glc (ball-and-stick representation) by the NB-loop. The maximum displacement for the NB-loop Cα atoms is 1.4 Å and 2.5 Å for the side chains. (c) Conformational rearrangements in the SB-loop region upon UDP-Glc binding. The apo- and UDP-Glc bound conformations are shown in black and purple, respectively. Residue R287, participating in the interlock mechanism, is highlighted in ball-and-stick conformation. The maximum displacement for the SB-loop Cα atoms is 3.3 Å and 12 Å for the side chains. (d) Overlay of apo-hUGP2 (semi-transparent, black bonds) and UDP-Glc bound hUGP1 (purple bonds) active site residues involved in product coordination. Numbers correspond to hUGP1 positions. See also Fig. S3 for stereo views of (a)–(d). (e) Conformation of the SB-loop region, comprising residues V282-F327, as observed in the octameric hUGP1·UDP-Glc complex (magenta) and after energy minimization of a single hUGP1 subunit (grey) (see Supplementary Methods).