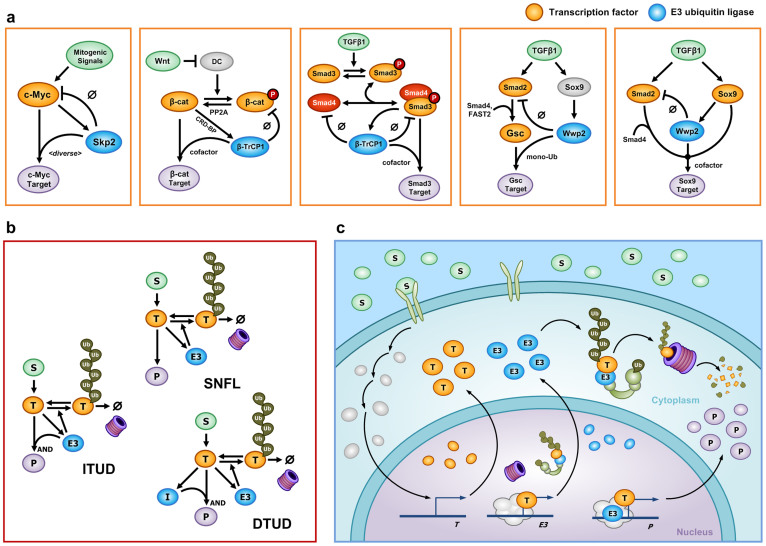
Figure 2. Biological examples and the generic mathematical model.
(a) Examples of E3 ubiquitin ligases (blue) that play paradoxical roles in proteolysis and transcriptional activation of a transcription factor (orange). (b) The mathematical model of ITUD. For comparative analysis, SNFL and DTUD are introduced as alternatives. Basal production and degradation of each component are not denoted in this diagram. (c) A detailed illustration of ITUD in a cell. This schematic diagram depicts a RING-type E3 ubiquitin ligase and its role as a cofactor in transcriptional activation. Other types of E3 proteins can be described differently. (b–c) S is an upstream signal; T is a transcription factor; E3 is an E3 ubiquitin ligase; P is the final product (system output); and I is an intermediate node.