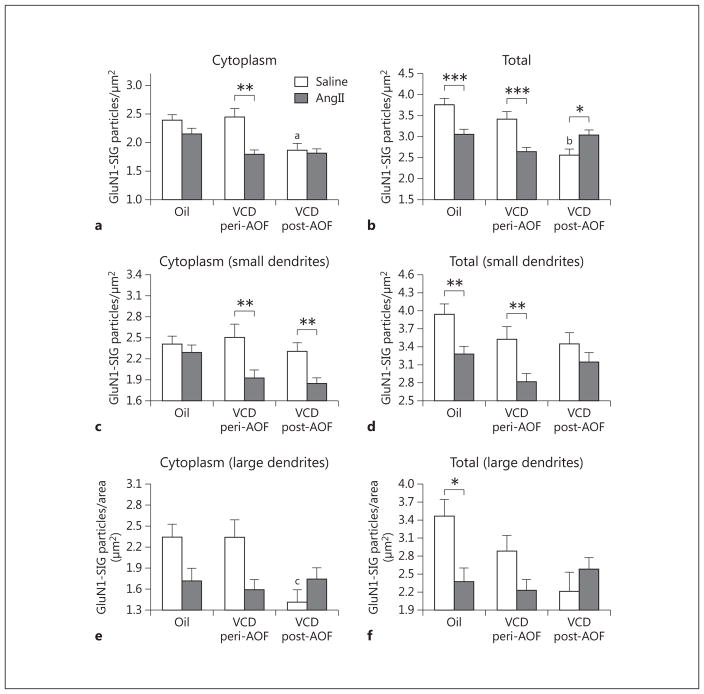
Fig. 4.
Slow-pressor AngII infusion differentially affects GluN1 density in ERβ-EGFP dendrites depending on AOF time point. a There is a significant decrease in the cytoplasmic density of GluN1-SIG particles in peri-AOF VCD mice following AngII infusion compared to peri-AOF VCD mice receiving saline. b The density of total GluN1-SIG particles in peri-AOF VCD mice given AngII compared to their peri-AOF VCD controls receiving saline is significantly reduced. In contrast, the density of total GluN1 particles in post-AOF VCD mice given AngII compared to their post-AOF VCD controls receiving saline is significantly increased. Oil-injected mice receiving AngII show a decrease in total GluN1 compared to those receiving oil and saline. c In small (<0.1 μm in diameter) ERβ-EGFP dendrites, AngII infusion results in a decrease in the cytoplasmic density of GluN1-SIG particles in peri- and post-AOF VCD mice. d In small ERβ-EGFP dendrites, the total number of GluN1-SIG particles is less in peri- and post-AOF VCD mice compared to oil-injected mice. Following AngII infusion, the density of the total number of GluN1-SIG particles decreases in oil-injected and peri-AOF VCD mice. e In large (>0.1 μm in diameter) ERβ-EGFP dendrites, the total number of GluN1-SIG particles in the cytoplasm of ERβ-EGFP dendrites in post-AOF VCD mice is significantly less compared to oil-injected and peri-AOF VCD mice. f Following AngII, the total number of GluN1-SIG particles in ERβ-EGFP dendrites significantly decreases in oil-injected mice. * p < 0.05; ** p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ap < 0.05 compared to saline + oil and saline + VCD peri-AOF; bp = 0.001 compared to saline + oil and p < 0.01 compared to saline peri-AOF VCD; cp = 0.01 compared to saline + oil and saline peri-AOF VCD.