Fig. 7. IRAK1 and IRAK2 have different functionalities in the human and mouse macrophage TLR signaling pathways.
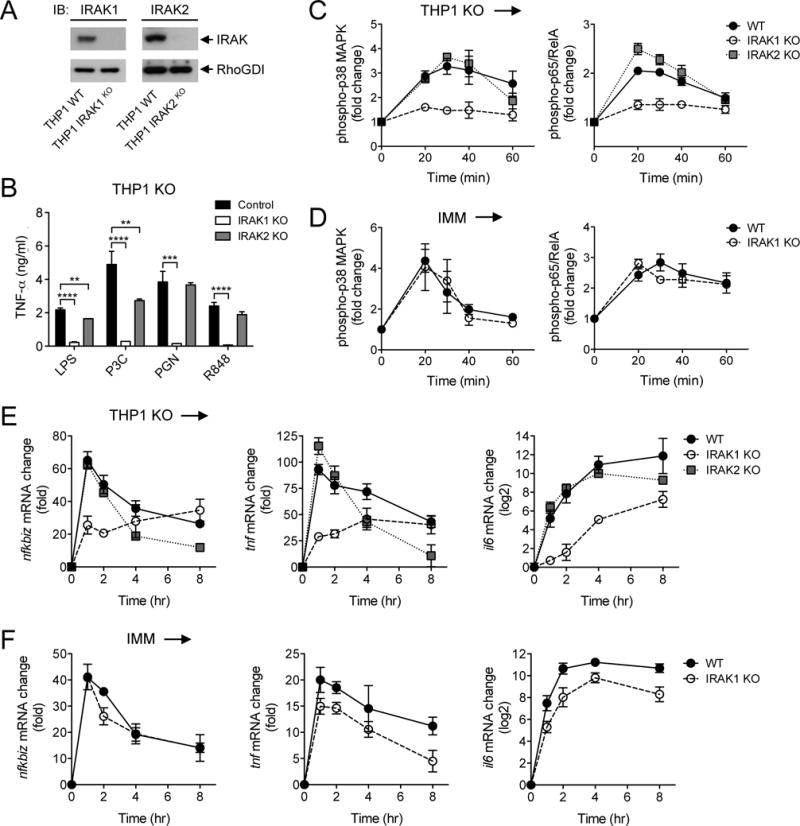
(A) The WT and indicated IRAK1 KO and IRAK2 KO THP1 cell lines were analyzed by Western blotting with antibody against IRAK proteins. RhoGDI was used as a loading control. Western blots are representative of two independent experiments. (B) The indicated control and IRAK KO THP1 cell lines were stimulated for 4 hours with LPS (10 ng/ml) before the amounts of TNF-α that they secreted were measured by ELISA. (C and D) The WT and indicated IRAK KO THP1 cell lines (C) and mouse IMMs (D) were stimulated with 500 nM P3C for the indicated times before the relative abundances of phosphorylated p38α MAPK (left) and p65 (right) were measured by phosphoflow cytometry. (E and F) The WT and indicated IRAK KO THP1 cell lines (E) and mouse IMMs (F) were stimulated with 500 nM P3C for the indicated times before the relative abundances of Nfkbiz (left), Tnf (middle), and Il6 (right) mRNAs were measured by qRT-PCR analysis. Data in (B) to (F) are means ± SD of two independent experiments. **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001, ****P < 0.0001 by two-tailed t test.
