Fig. 8. Differential human and mouse IRAK dependencies are reflected in responses to gram-negative bacterial infection and in ligand-induced signaling complexes.
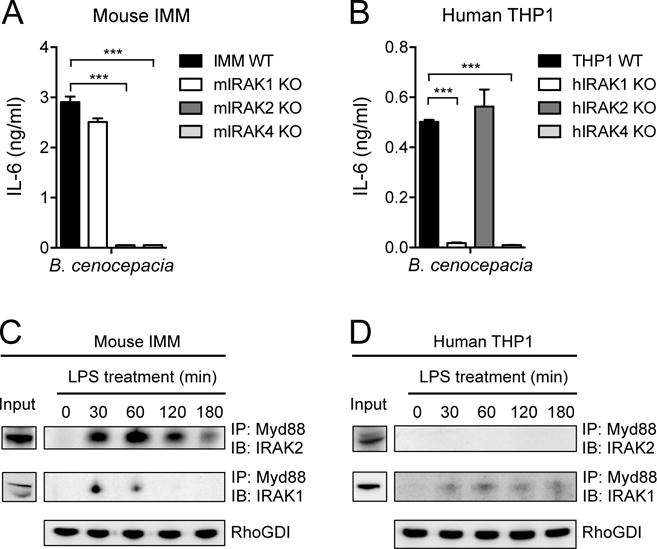
(A and B) IMMs from WT mice and the indicated IRAK KO mice (A) and the WT and indicated IRAK KO THP1 cell lines (B) were infected with B. cenocepacia at an MOI of 1. Twenty hours later, the amounts of IL-6 secreted by the cells were measured by ELISA. (C and D) IMMs from IRAK4 KO mice (C) and IRAK4 KO THP1 cells (D) were stably transduced with retrovirus expressing either mouse IRAK4-mCitrine or human IRAK4-mCherry, respectively. The cells were then treated with LPS (10 ng/ml) for the indicated times before cell lysates were subjected to immunoprecipitation (IP) with antibodies against Myd88 and analyzed by Western blotting (IB) with antibodies against either IRAK1 or IRAK2. RhoGDI is shown as an input control for the Myd88 immunoprecipitation. Western blots are representative of three independent experiments. Data in (A) and (B) are means ± SD of two independent experiments. ***P < 0.001 by two-tailed t test.
