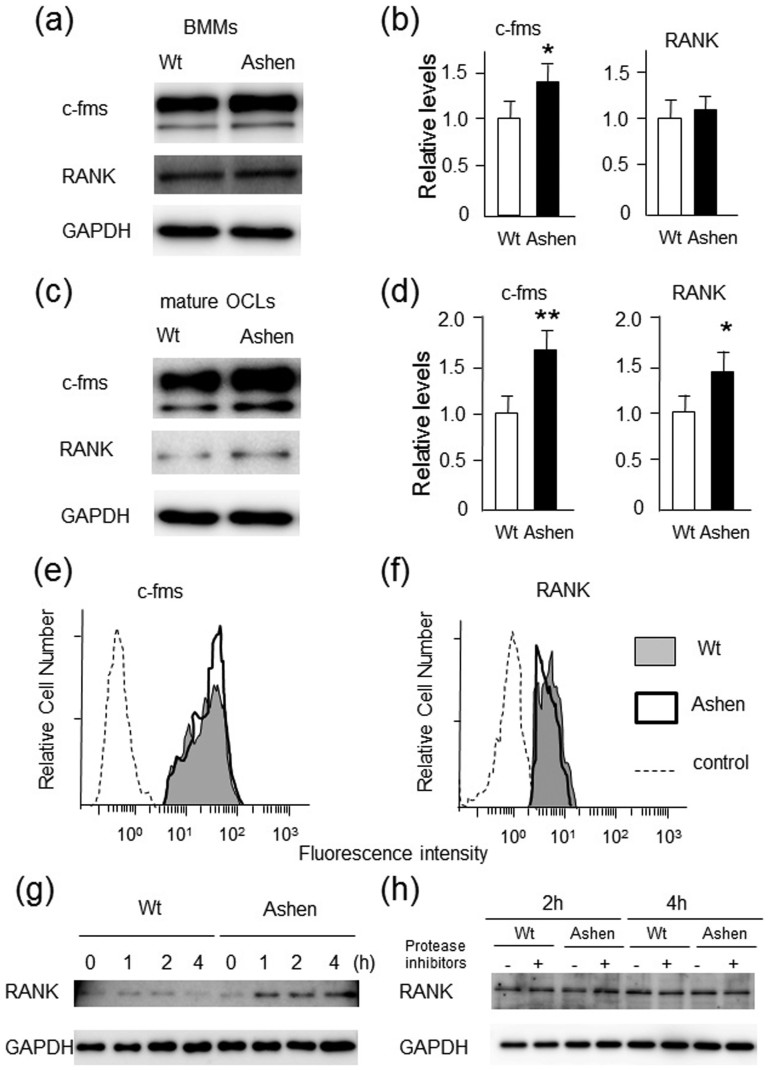
Figure 5. Expression levels of RANK and c-fms in BMMs or OCLs from wild-type and ashen mice.
BMMs were prepared as per the method described in “Experimental Procedures”. The OCLs were further differentiated from BMMs cultured with RANKL (50 ng/ml) and M-CSF (30 ng/ml) for the 72 h. The same protein amounts of BMM-lysates (a) or OCL-lysates (c) were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western blotting with antibodies against RANK, c-fms, and GAPDH. (b, d). Densitometric analysis for the quantification of each protein in the cell lysate of both cell types. The relative levels were defined as the chemiluminescence intensity per mm2 measured by LAS4000-mini. The data are represented as the mean ± S.D. of values from four independent experiments. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 for the indicated comparison. (e, f) Flow cytometric analysis of surface levels of c-fms (e) or RANK (f) in BMMs. The cells were stained for cell surface with specific antibody against c-fms or RANK, and subsequently stained with a second antibody conjugated with PE. Data are representative of four independent experiments. (g) Down-regulation of RANK in BMMs from wild-type and ashen mice. Both the BMMs were treated with RANKL (50 ng/ml), and further incubated at 37°C for the indicated times. The cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western blotting with antibodies against RANK and GAPDH. (h) Degradation of RANK by lysosomes in BMMs from wild-type and ashen mice. Both the BMMs were treated with RANKL (50 ng/ml), and further incubated at 37°C in the absence or presence of E-64 (10 micro g/ml) and pepstain (10 micro g/ml) for the indicated times. The cell lysates were subjected to SDS-PAGE followed by western blotting with antibodies against RANK and GAPDH.