Figure 6. Antiviral treatment in VZV disease.
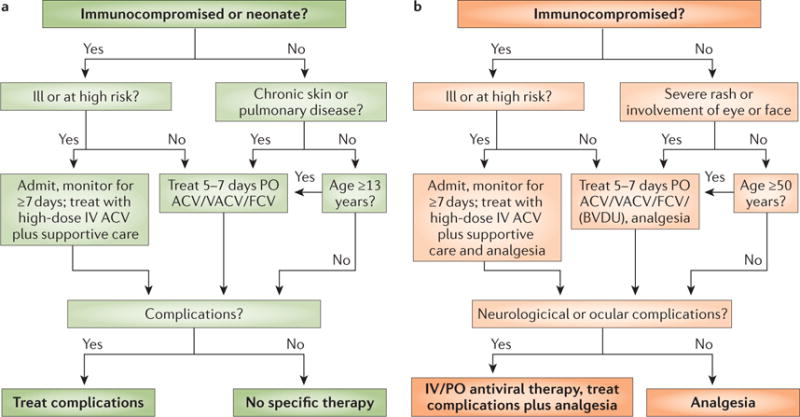
a | Antiviral treatment of varicella is indicated in immunocompromised individuals, neonates, patients with chronic skin or lung diseases and in individuals aged >13 years. Patients receive oral acyclovir (ACV), valaciclovir (VACV) or famciclovir (FCV; not approved by the FDA for use in children) unless they are clinically ill or at high risk (most immunocompromised patients are considered to be at high risk, except those who receive long-term, effective immunoglobulin replacement therapy or those who received only mildly immunosuppressive drugs a long time ago). Ill and high risk patients receive intravenous (IV) ACV or foscarnet if the infection is caused by ACV-resistant VZV. Intravenous treatment always needs careful consideration of kidney function. b | The treatment of zoster follows a similar algorithm; here compromised immunity, illness, severe rash, involvement of eyes or face, and other complications are indications for antiviral treatment. In addition to ACV, VACV and FCV, brivudin (BVDU; not approved by the FDA) might be used. Patients who develop varicella or zoster in hospital will generally receive antiviral therapy as part of an infection control strategy. PO, per os (oral administration).
