Figure 7. Mode of action of acyclovir.
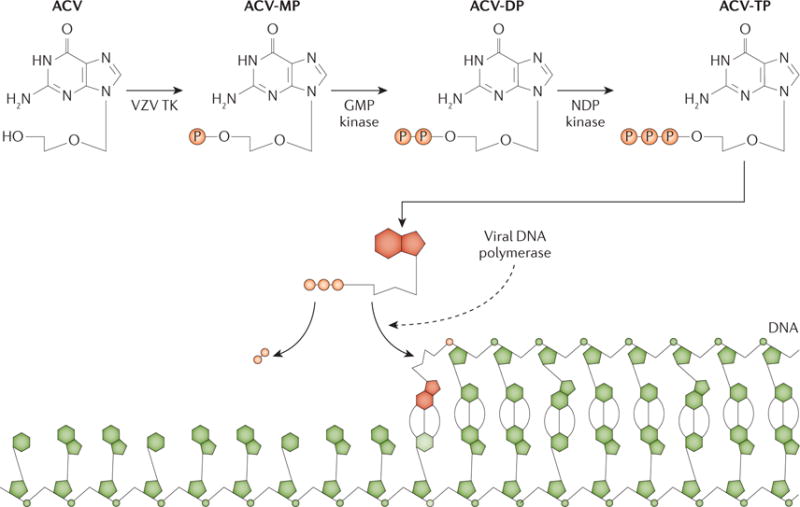
In cells infected with varicella zoster virus (VZV), acyclovir (ACV) is converted by the viral thymidine kinase (TK) to ACV-monophosphate (ACV-MP). The cellular enzymes guanylate (GMP) kinase and nucleoside-diphosphate (NDP) kinase further catalyse the production of ACV-diphosphate (ACV-DP) and ACV-triphosphate (ACV-TP). When the viral DNA polymerase uses ACV-TP, elongation of the DNA chain is terminated. Adapted from REF 211, Nature Publishing Group.
