Figure 1.
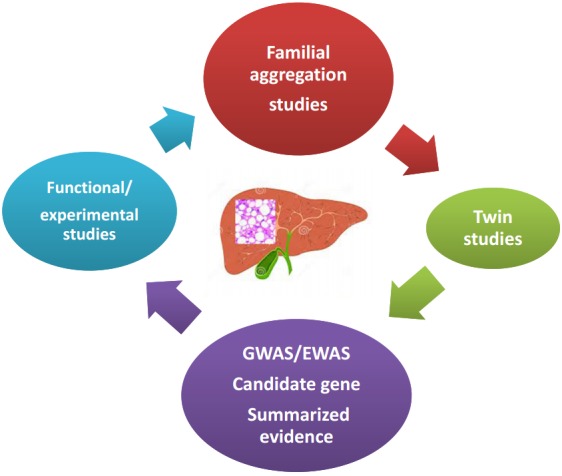
NAFLD, is a polygenic and heritable disease. Picture summarizes different approaches that have been used to date to explore the genetic component of NAFLD. Familial aggregation studies are typically conducted in order to identify the genetic component of complex diseases; the goal of this strategy is to assess clustering of the disease within families. Twin genetic studies have also contributed to the knowledge of the genetic susceptibility of complex diseases; large twin registries are highly beneficial resources for comparing the genetic risk of a disease between monozygotic and dizygotic twins. GWAS and EWAS, which include a global survey of sequence variants across the entire genome or variants in the coding regions, respectively, have shed light onto the genetic component of NAFLD, as well as other complex diseases in the last decade. Candidate gene association studies are focused on loci selected on the basis of their known or presumed function or on their biological plausibility in the disease pathophysiology. Finally, functional and experimental studies aim to provide mechanistic insights into the role of a variant or locus of interest in the explored phenotype. NAFLD, nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; GWAS, genome-wide association study; EWAS, exome-wide association study.
