Fig. 6. Schematic images of the superficial veins of the lower extremities.
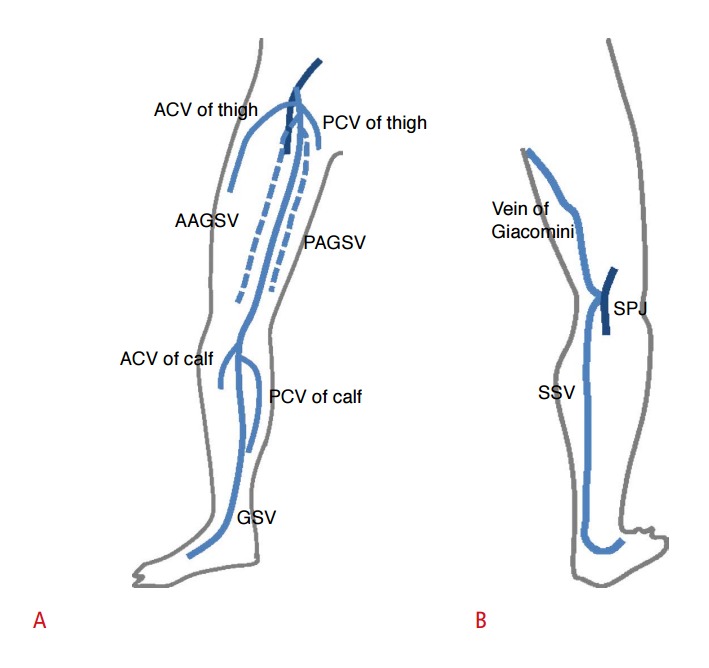
A. The great saphenous vein (GSV) arises from the medial aspect of the dorsal pedal venous arch, ascends anteriorly to the medial malleolus, passes posteromedially to the knee, and ascends medially in the thigh to join the common femoral vein through the saphenofemoral junction. Tributaries of the GSV are named according to their course. A tributary parallel to the GSV is called an accessory GSV. A tributary that courses obliquely is called a circumflex vein. ACV, anterior circumflex vein; PCV, posterior circumflex vein; AAGSV, anterior accessory great saphenous vein; PAGSV, posterior accessory great saphenous vein. B. The small saphenous vein (SSV) arises from the dorsal pedal arch and ascends along the middle of the calf and ends in the popliteal vein through the saphenopopliteal junction (SPJ). Before it penetrates the muscular fascia, the SSV may branch out a cranial extension, known as the vein of Giacomini, which goes upward to join the GSV.
