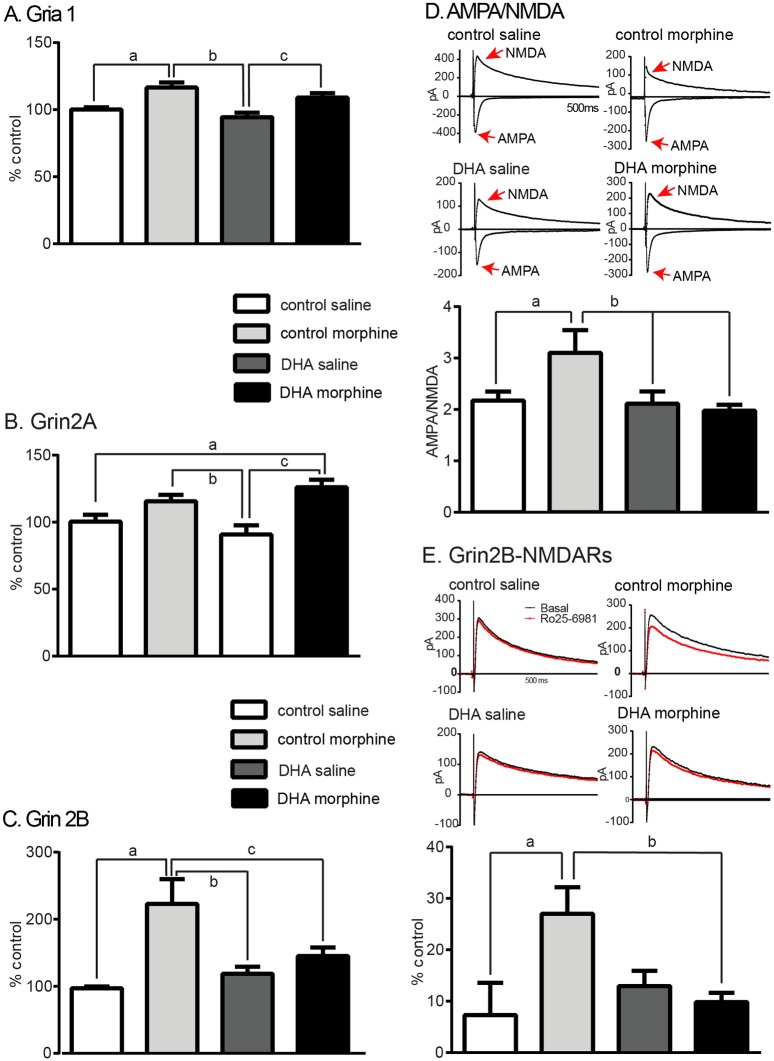
Fig 3. Dietary DHA reverses the effects of morphine on specific striatal glutamate receptor subunit expression and function.
A. Gria 1. DHA supplementation did not alter the morphine-induced increase in Gria1 transcript levels. a; p<0.01, b; p<0.001, c: p<0.05 B. Grin 2A. DHA supplementation did not alter the effect of morphine on Grin2A expression which increased following morphine in control or DHA groups. a and b; p<0.05, c; p<0.01. C. Grin 2B DHA supplementation reduced the morphine-induced increase in Grin2B expression. a; p<0.0001, b; p<0.01, c; p<0.005. D. AMPA/NMDA ratio This index of glutamatergic signaling, assessed at -70 and +40mV, increased following morphine. DHA reduced this increase. a and b; p<0.05. E. Grin2B-NMDARs NMDARs were recording in the absence and presence of a Grin2B antagonist, Ro25-6981 (1μM). Morphine increased Grin2B-containing NMDARs and this was reduced following DHA, a; p<0.01, b; p<0.01.