Figure 1.
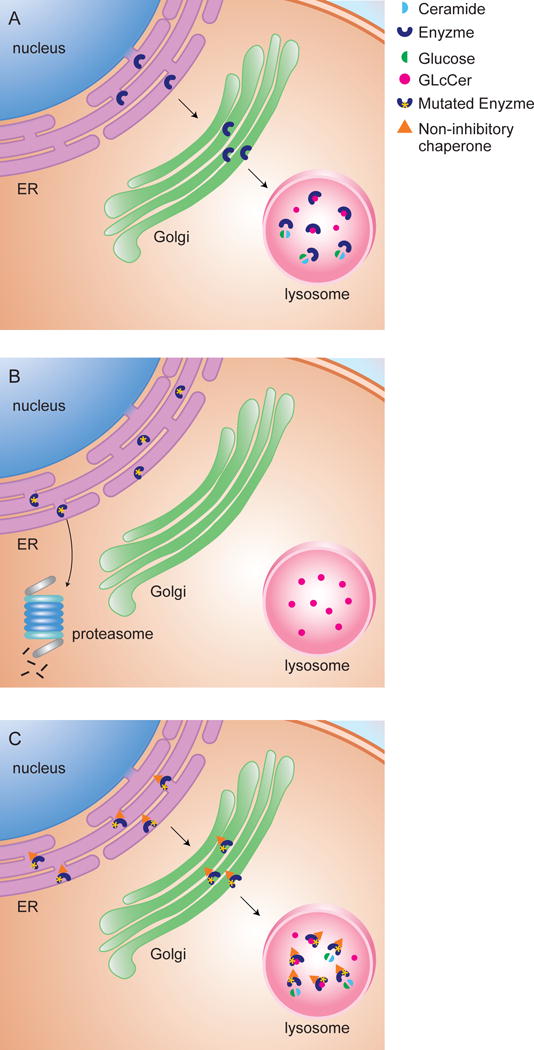
Non-inhibitory chaperones for enhancement of GCase. (A) Wild-type GCase is folded in the ER and translocated to lysosomes where it turns over its substrate. (B) Mutant GCase is misfolded in the ER and undergoes premature degradation in the proteasome with subsequent lysosomal accumulation. (C) Non-inhibitory chaperones facilitate folding and stabilization of mutant GCase in the ER as well as translocation to lysosomes where the residual activity of mutant enzyme is able to turn over substrate.
