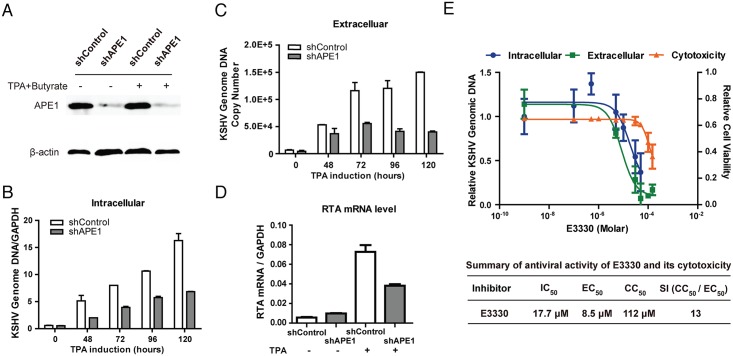
Fig 1. Validation of the role of APE1 redox function in KSHV DNA replication and virion production using shRNA-mediated silencing of APE1 expression and a specific APE1 inhibitor.
(A) An APE1 shRNA lentivirus targeting the 3’UTR of APE1 (shAPE1), along with a non-targeting control shRNA lentivirus (shControl), were transduced into BCBL-1 cells. The effects of the shRNA on APE1 and β-actin gene expression were determined by Western blot. (B) The cells stably expressing APE1 and control shRNAs were induced by TPA for lytic viral replication. KSHV lytic DNA replication was evaluated at different time points up to 120 hour post-induction by real-time PCR with specific primers detecting ORF73 and GAPDH sequences. (C) KSHV virion production was assessed by determining encapsidated KSHV genomic DNA in the media 5 days after induction. (D) The RTA mRNA levels were also determined using qRT-PCR at 48 hour post-induction. (E) An APE1 redox inhibitor E3330 was examined for the effect on KSHV DNA replication, virion production and its associated cytotoxicity. The half maximal inhibitory concentration (IC50) of E3330 for KSHV DNA replication, the half maximal effective concentration (EC50) for blocking KSHV virion production and the half maximal cytotoxic concentration (EC50) were determined and selectivity index (SI)) was calculated as the ratio of CC50/EC50. The mean value of each datum was obtained from three independent experiments and presented with standard deviation. Statistical analysis was performed using t test, P-value was calculated by GraphPad Prism.