Fig. 4. Separation performance of SNF/HAP membranes.
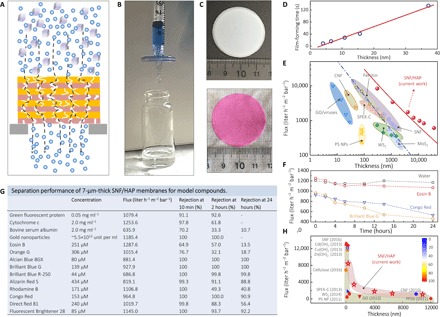
(A) Cross-sectional representation of a multilayer SNF/HAP membrane to filter compounds. (B) Image of the SNF/HAP-based syringe nanofilter, which successfully rejected Alcian Blue 8GX with a rejection of 98%. The detailed structures of SNF/HAP membranes formed on microfilters can be found in fig. S16B. (C) SNF/HAP nanofiltration membrane before (top) and after (bottom) filtration with 20 ml of 5 mM Rhodamine B solution. (D) Linear relationship between film thickness and film formation processing time. (E) Thickness-dependent changes in permeability to pure water for the SNF/HAP membranes and other previously reported membranes. The blue dash-dot line is a fitted curve using the Hagen-Poiseuille equation with uniform structure (9, 44). The red solid line is a fitted curve using Eq. 1 for multilayer membrane (see also section S8). (F) Time-dependent changes in the flux of water and dye solution within 24 hours of flow. (G) Separation performance of 7-μm-thick SNF/HAP membranes for dyes, proteins, and colloids after 10 min, 2 hours, and 24 hours of flow. The flux listed in the table was calculated from the filtration of model compound solutions. The filtration pressure was kept at 80 kPa in all these tests. Several dye solutions have lower flux than pure water, likely because of their large molecular size, which would be responsible for blocking the pores of membranes. (H) Comparison of the 5-nm gold nanoparticle separation performance of SNF/HAP membranes to that of other filtration membrane materials. The rejection is represented by the color of the pattern. The blue and red are 0 and 100% rejection, respectively. Cd(OH)2, Cu(OH)2, and Zn(OH)2 are Cd(OH)2, Cu(OH)2, and Zn(OH)2 nanofibers. Cellulose, cellulose nanofibers; SPEK-C, sulfonated polyetherketone with cardo groups; WS2, chemically exfoliated tungsten disulfide nanosheets; PS NP, polystyrene nanoparticles; GO, graphene oxide sheets; CNF, carbonaceous nanofiber; PP2b, 5,5′-bis(1-ethynyl-7 polyethylene glycol-N,N′-bis(ethylpropyl) perylene-3,4,9,10-tetracarboxylic diimide)-2,2′-bipyridine.
