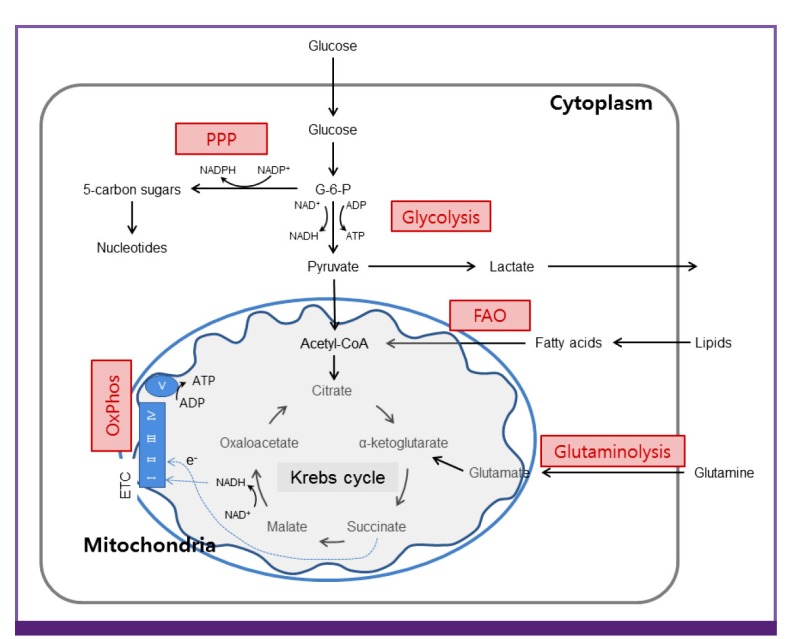
Figure 1.
Integration of metabolic pathways
Glucose is metabolized to pyruvate through the glycolysis. Pyruvate (and fatty acids) enters the mitochondria where they are converted to acetyl-CoA. This enters the Krebs cycle that donates electrons to electron transport chain. Through OxPhos, electrons are sequentially transferred to generate a H+ gradient across the inner mitochondrial membrane, which drives the synthesis ATP. In addition to the glycolysis, cells have the ability to metabolize alternative substrates, such as lipids and glutamine. FAO and glutaminolysis replenish the Krebs cycle intermediates acetyl-CoA and α-ketoglutarate, respectively, thereby fueling OxPhos. PPP generates riboses for nucleotides synthesis.
PPP, pentose phosphate pathway; OxPhos, oxidative phosphorylation; FAO, fatty acid β-oxidation; ADP, adenosine diphosphate; ATP, adenosine triphosphate; ETC, electron transport chain.