Fig. 2.
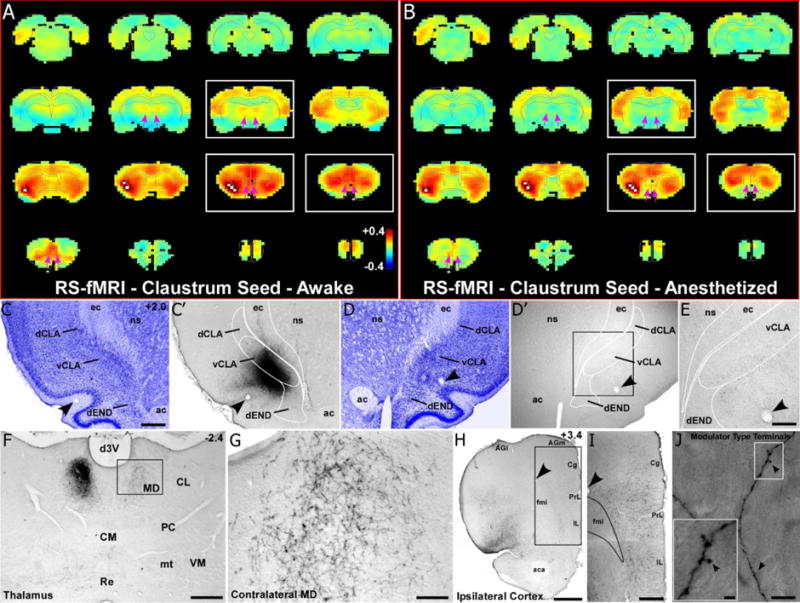
RS-fMRI in the awake state reveals bilateral functional connections of the claustrum that are lost during anesthesia. (a) Average RS-fMRI of awake rats, showing a unilateral seed (white voxels) based analysis of the claustrum. Strong functional connectivity was observed bilaterally between the claustrum, mediodorsal thalamus (MD), medial prefrontal cortex (mPFC), and several other cortical areas (including retrosplenial, sensorimotor and multimodal regions). The claustrum also displayed functional connectivity with the contralateral claustrum. White boxes correspond to sections shown in tracing data. Color bar represents correlation coefficients and applies to panel b as well. (b) Unilateral seed analysis of claustrum in anesthetized condition revealed abolished functional connectivity with MD and reduced functional connectivity with mPFC (see pink arrows). (c) Nissl stained section showing cytoarchitecture of the dorsal and ventral claustrum (dCLA, vCLA) and dorsal endopiriform nucleus (dEND) with adjacent section (c′) showing an anterograde tracer injection (BDA) primarily in vCLA (abbreviations: ec, external capsule; ns, neostriatum; ac, anterior commissure). Scale bar in c, 500μm. (c–e) Labeling is absent in the contralateral claustrum despite a strong functional connection detected by RS-fMRI in panels a and b. Scale bar in e, 250μm. (f–g) Bilateral labeling in MD, which matches bilateral functional connectivity. Scale bars: 500μm in f; 100μm in g. (h–i) Terminal labeling in ipsilateral mPFC, distributed across all layers of cortex (abbreviations: AGl, agranular lateral; AGm, agranular medial; Cg, cingulate; PrL, prelimbic; IL, infralimbic; fmi, forceps minor of the corpus callosum; aca, anterior commissure). Scale bars: 1mm in h; 500μm in i) (j) Claustro-cortical synaptic terminals have modulator-type morphology (black arrows). Scale bars: 10μm in (j); 2μm in inset.
