Fig. 9.
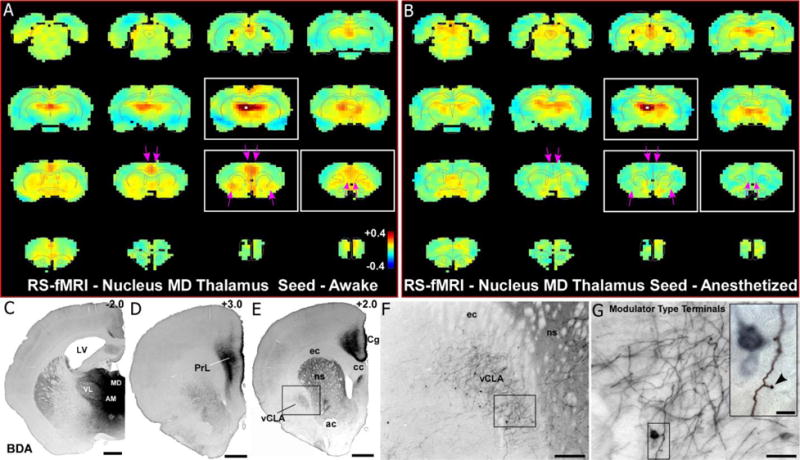
RS-fMRI analysis in the awake state reveals functional connections with the MD thalamus that are lost during anesthesia. (a) Average RS-fMRI of awake rats, with a unilateral seed (white voxels) in mediodorsal thalamus (MD). Strong functional connectivity was observed between MD and bilateral regions of mPFC and claustrum. Color bar represents correlation coefficients and applies to panel b as well. (b) Anesthesia abolished functional connectivity with both mPFC and claustrum (see pink arrows). (c–e) Anterograde tracer injection (panel c) into MD shows anatomical connectivity with mPFC (prelimbic cortex, PrL; cingulate cortex, Cg) shown in panels d and e, as well as claustrum (panel e). Scale bars: 1mm in c, d, e. Abbreviations: AM, anteromedial nucleus; VL, ventrolateral nucleus; LV, lateral ventricle; cc, corpus callosum; ec, external capsule; ns, neostriatum; ac, anterior commissure. (f) Higher magnification image of claustrum labeling from inset in e, showing both anterogradely-labeled fibers and retrogradely-labeled neurons. Scale bar: 250μm. (g) Higher magnification image of labeling from inset in f, showing projections from MD to claustrum are thin fibers with small modulator type terminals. Scale bars: 50μm in g; 10μm in inset.
