FIGURE 6.
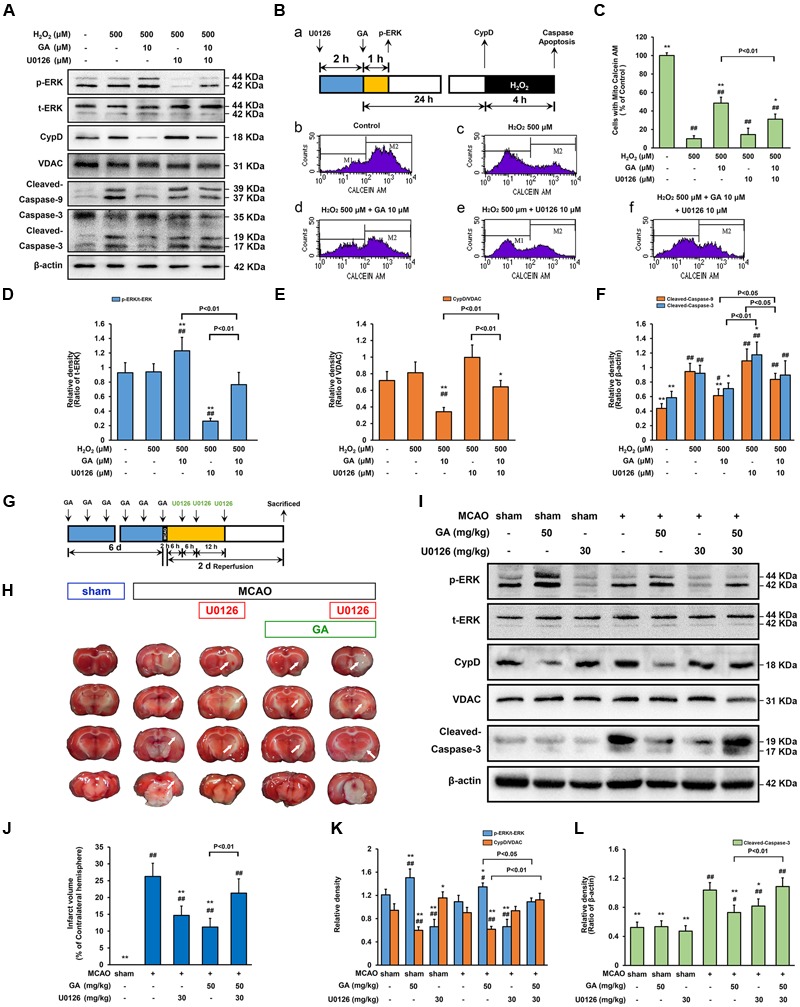
Extracellular signal-regulated kinases mediates GA-induced cytoprotective effect via CypD downregulation. ERK is necessary for GA to prevent H2O2-induced apoptosis via CypD downregulation. (A) The phosphorylation of ERK and the expression of CypD were determined by immunoblotting. t-ERK, VDAC, and β-actin were used as a loading control. The design for the in vitro experiment in this figure was shown in (B-a). (B-b–f) MPTP determined by Calcein-CoCl2 assay and (C) quantification by flow cytometry (n = 4). (D–F) Histogram showing the relative intensities of the bands in each sample was semi-quantification by quantity software (n = 4). ##P < 0.01, #P < 0.05 versus control group. ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗P < 0.05 versus H2O2 group. ERK signaling triggered by GA were involved in MCAO-mediated apoptosis in rats. (G) The design for the in vivo experiment in this figure. (H) Representative TTC-stained coronal brain sections; white indicates infarcted tissue. (I) The phosphorylation of ERK and the expression of CypD were determined by immunoblotting. (J) Histogram showing the infarct volume (% of contralateral hemisphere) in TTC-stained brain sections (n = 8). (K,L) Quantification the bands in each sample was semi-quantification by quantity software (n = 4). ##P < 0.01, #P < 0.05 versus sham group. ∗∗P < 0.01, ∗P < 0.05 versus MCAO group. Data reported as the means ± SD. P values were obtained using two-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) test.
