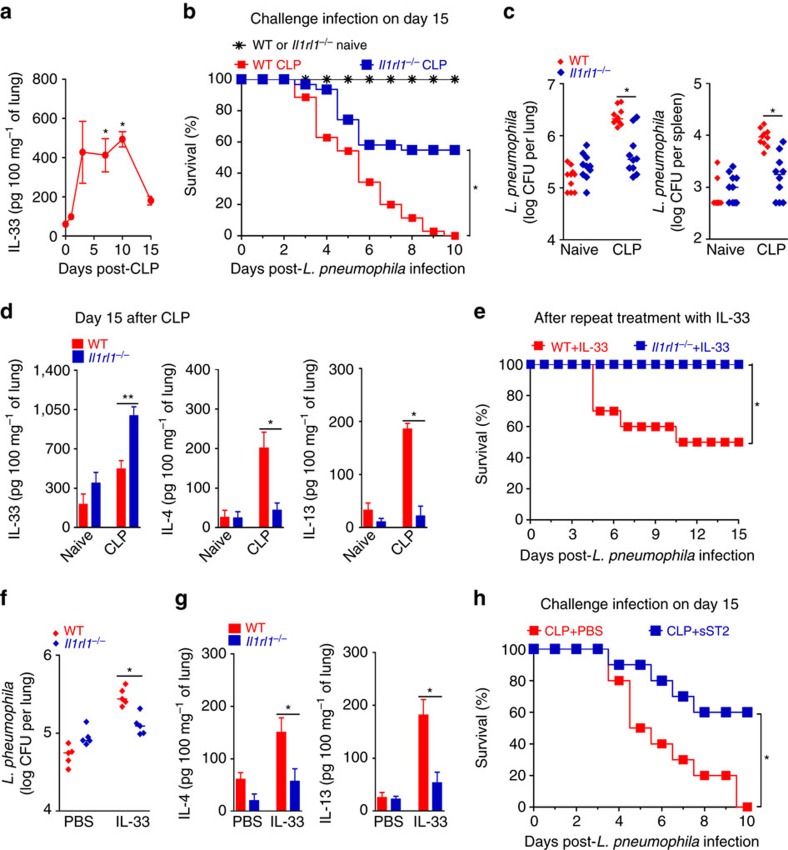
Figure 1. IL-33 is critical for sepsis-induced immunosuppression.
(a) IL-33 concentrations in the lungs of BALB/c mice undergoing CLP and antibiotic treatment were determined by ELISA (n≥4 mice per group). (b–d) Surviving BALB/c and Il1rl1−/− mice undergoing CLP and antibiotics were challenged with L. pneumophila 15 days after CLP. (b) Survival curves after challenge (n=30 mice for naive group, n=35 mice for WT CLP group and n=31 mice for Il1rl1−/− CLP group). (c) Bacterial loads in lungs and spleen 24 h after challenge (n=10 mice per group). (d) Concentrations of IL-4, IL-13 and IL-33 in the lungs 15 days after CLP determined by ELISA (n≥4 mice per group). (e–g) BALB/c and Il1rl1−/− mice were inoculated i.n. with IL-33 or PBS for 4 consecutive days and challenged i.n. 2 days later with L. pneumophila. (e) Survival curves (n=10 mice per group). (f) Bacterial load in the lung tissue 48 h after challenge (n=5 mice per group). (g) IL-4 and IL-13 concentrations in the lung tissue 48 h after challenge (n=5 mice per group). (h) BALB/c mice undergoing CLP and antibiotics were injected i.p. with sST2 or PBS. The sepsis-surviving mice were challenged with L. pneumophila on day 15 (n=10 mice per group). *P<0.05 and **P<0.01 (one-way ANOVA result with Dunnett posthoc tests in a, Mantel–Cox log-rank test in b,e,h, Mann–Whitney U test in c,f and two-tailed unpaired Student's t-test in d,g). Data are one experiment (h); or representative of two (a,b,g) or three (d,f) independent experiments with similar results; or pooled from two (e) or six (b) independent experiments (mean±s.e.m. in a,d,g and median in c,f).