Fig. 5.
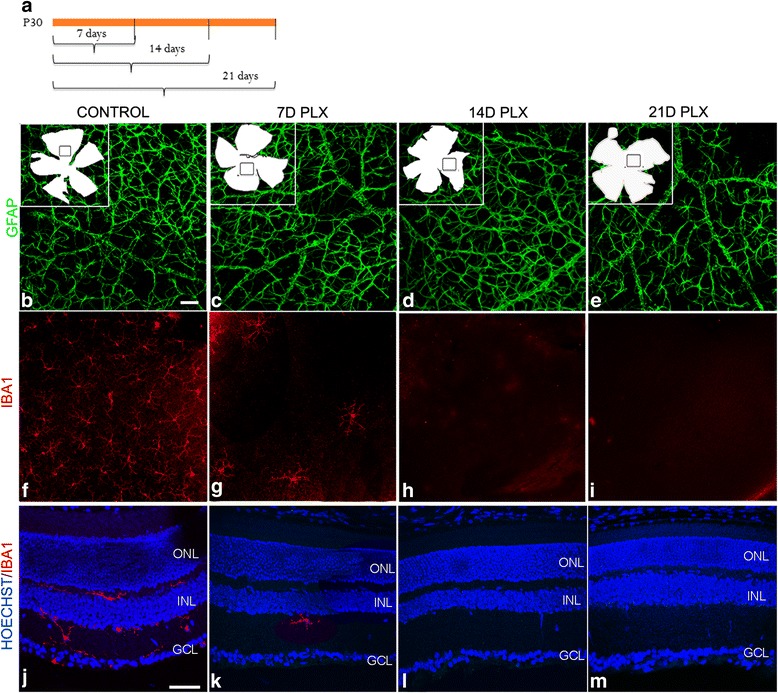
PLX ablates microglia in the retina. Mice were fed with chow-containing PLX or vehicle dye to determine ablation of microglia in the retina. a Schematic describing the time points for which the mice were fed with chow-containing PLX, following which eyes were harvested. Retinal flatmounts prepared from the eyes harvested at 7, 14, and 21 days were labeled for GFAP or IBA1 (b–i). Insets in b–e indicate the flatmount outline and from where the images (b–i) was taken. While GFAP did not show any difference between the stages examine (b–e), there was a significant decrease in IBA1 label in mice kept on PLX diet for 7 days (f, g). By 14 days, no IBA1 label was found in the retinal flatmount and this absence persisted into the 21-day time point (h, i). Retinal sections control and PLX-treated mice labeled for IBA1 to show loss of microglia in the deeper layers of the retina (j–m). Statistical analysis was performed by unpaired Student’s t test. *p value <0.05. Magnification bar in b = 50 μm, for images b–i. Magnification bar in j = 50 μm, for images j–m. Abbreviations: GFAP glial fibrillary acidic protein, IBA1 ionized calcium-binding adapter molecule 1
