Figure 1.
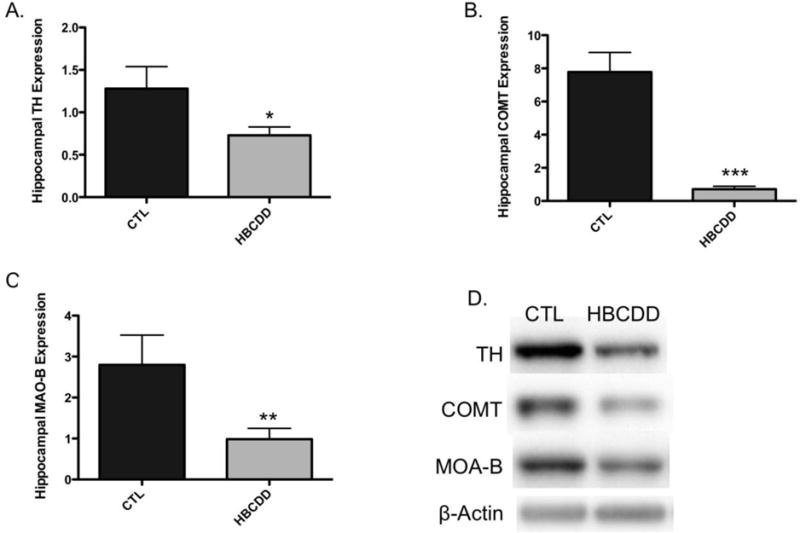
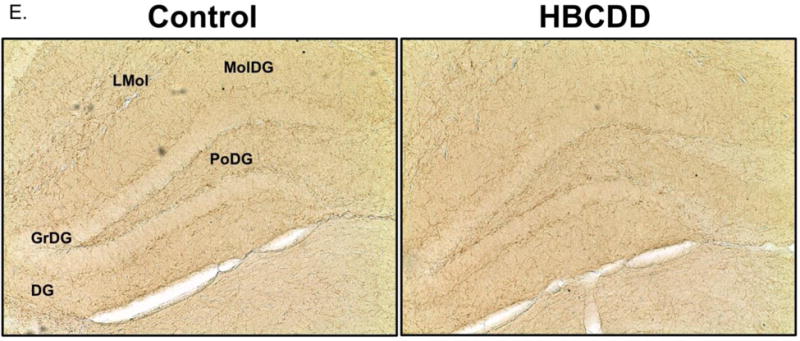
Exposure to HBCDD causes a reduction in enzymes critical to dopamine synthesis and degradation in the hippocampus. Animals received 0 or 25 mg/kg HBCDD for 6 weeks and were sacrificed 6 weeks later and evaluated for alterations in (A) TH, (B) COMT, and (C) MAO-B. (D) Representative immunoblot bands for each marker. Data represents mean ± SEM (6 animals per experimental group). (E) Representative immunohistochemical images of TH expression in the hippocampus of control and HBCDD treated animals. *Values that are significantly different from control (p<0.05). **Values that are significantly different from control (p<0.01). ***Values that are significantly different from control (p<0.001). DG: Dentate gyrus, GrDG: Granule cell layer of the dentate gyrus, LMol: Lacunosum molecular layer of CA1, MolDG: Molecular cell layer of the dentate gyrus, PoDG: Polymorph cell layer of the dentate gyrus.
