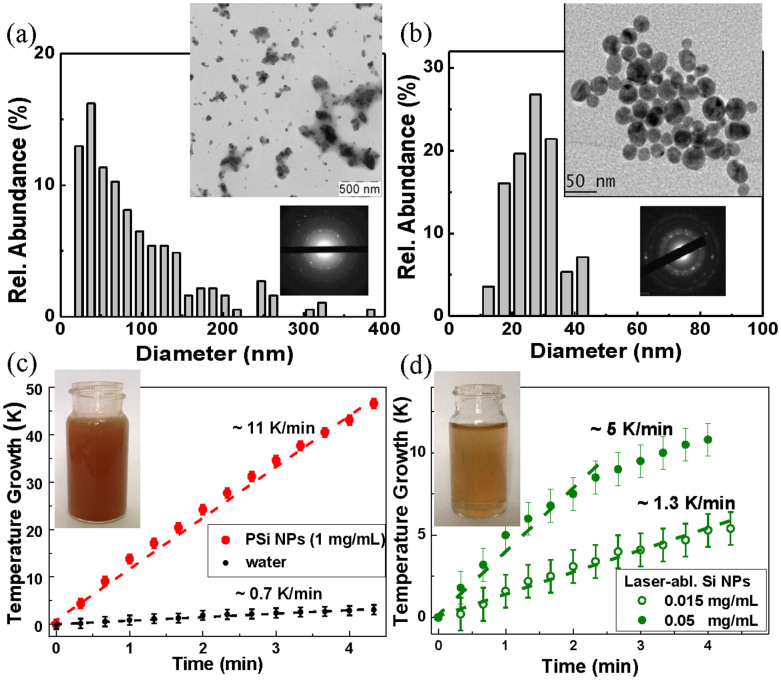
Figure 2. Si nanoparticles as nanosensitizers for RF radiation-induced hyperthermia.
(a) TEM image (inset), electron diffraction pattern obtained in the “transmission” geometry (inset) and corresponding size distribution of porous silicon (PSi) nanoparticles prepared by mechanical milling of electrochemically prepared porous silicon; (b) TEM image (inset), electron diffraction pattern (inset) and corresponding size distribution of NPs prepared by laser ablation from a Si target in deionized water; (c) Temperature growth of an aqueous suspension of PSi NPs with concentration of 1 mg/mL (red curve) and distilled water (black) under RF irradiation with intensity of 5 W/cm2 versus the RF irradiation time; (d) the same dependence for laser-ablated Si-based NPs with concentration of 0.015 mg/mL (open green circles) and 0.05 mg/mL (closed green circles). Insets in panels (c) and (d) show glass cuvettes with the NP suspensions of PSi and LA-Si, respectively.