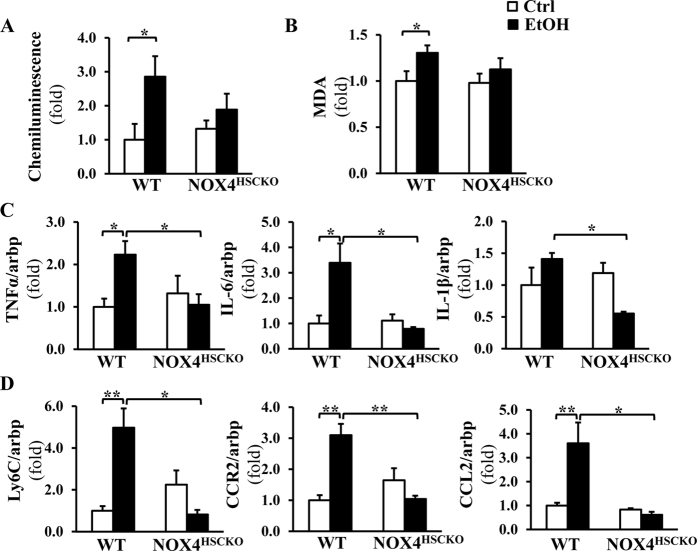
Figure 2. CCR2/CCL2 and inflammatory cytokines are attenuated in the NOX4HSCKO mice on ethanol diet.
ROS production and lipid peroxidation were measured by the lucigenin chemiluminescence assay (A) and MDA quantitative assays, respectively (B). Chemiluminescence results and MDA concentrations were normalized for protein concentrations and the results show increased ROS production and lipid peroxidation in WT mice on alcohol diet, but no significant change in NOX4HSCKOmice (a trend towards less ROS and MDA, albeit not statistically significant). The expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines TNF-α, IL-1β, and IL-6 (C), Ly6C, CCR2, and CCL2 (D) were studied by RT-qPCR, and were significantly increased in WT mice on ethanol diet (TNFα (2.4 ± 0.3), IL-6 (2.8 ± 0.3), CCL2 (2.2 ± 0.5), IL-1β (1.4 ± 0.1), Ly6C (4.9 ± 0.9) and CCR2 (3.1 ± 0.3), whereas no induction was observed in NOX4HSCKOmice (Mean ± SEM, N = 3–4, *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).