Figure 1. Characterization of BVVL iPSC-derived motor neurons (MNs).
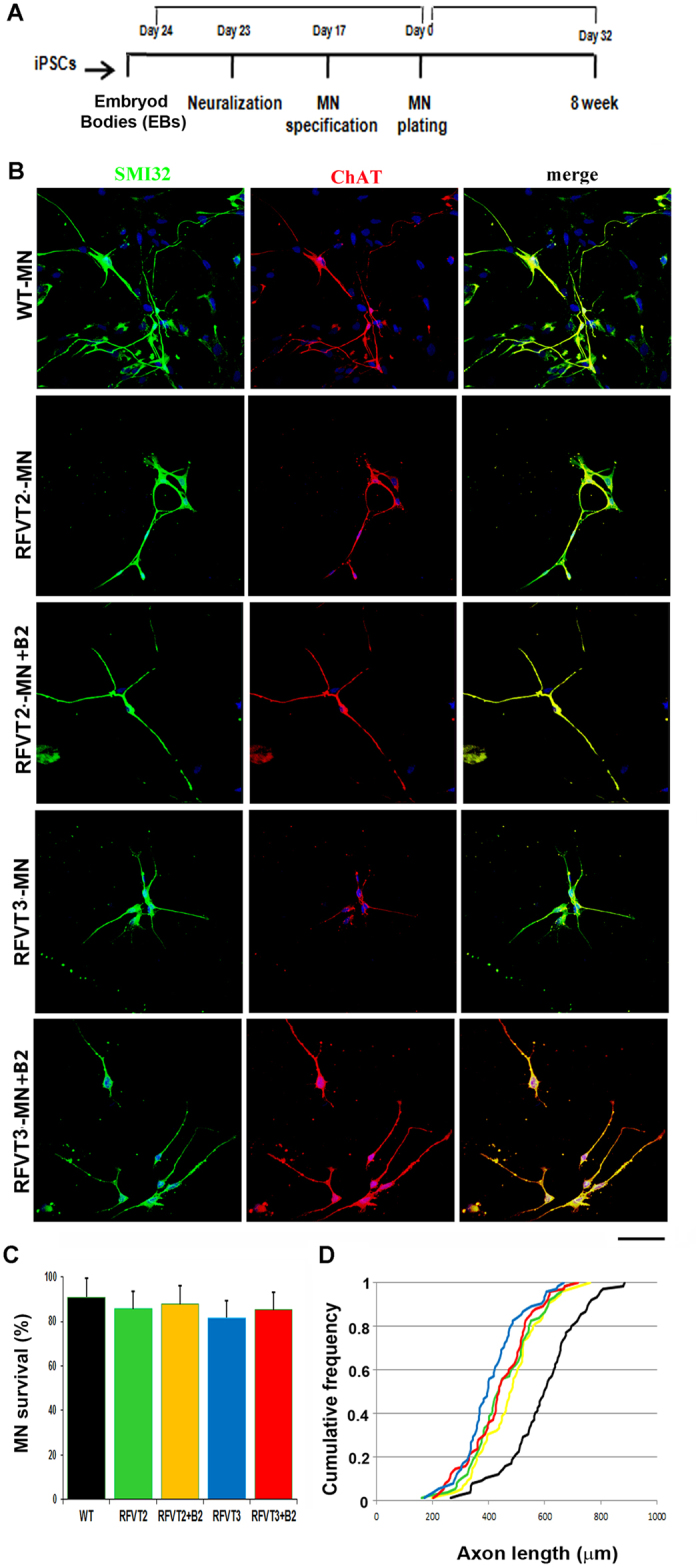
(A) Experimental outline for WT and BVVL-MN differentiation and characterization. (B) Immunocytochemistry of WT-MNs and BVVL-MNs (RFVT2-MNs, RFVT3-MNs). The cells were positive for typical MN markers: SMI32 (green) and ChAT (red) (merge, yellow signal). Nuclei are labeled with DAPI (blue). The analyses were performed in basal condition and after supplementation with riboflavin (B2). Scale bar: 75 μm. (C,D) Morphometric analysis of WT-MNs and BVVL-MNs. (C) Eight weeks after differentiation, BVVL-MN survival was not significantly reduced compared with WT-MNs (Student t test). Values represent means ± SD from five independent experiments performed in triplicate. (D) After 8 weeks of culture, BVVL-MNs exhibited a significantly reduced axon elongation with respect to WT cells. The improvement of axon elongation was observed after riboflavin supplementation, in particular in the patient with mutant RFVT3. Kolmogorov–Smirnov test. Five independent experiments performed in triplicate.
