Fig. 5. In vitro model of activated CD8+ T cell-mediated Rae-1 restoration.
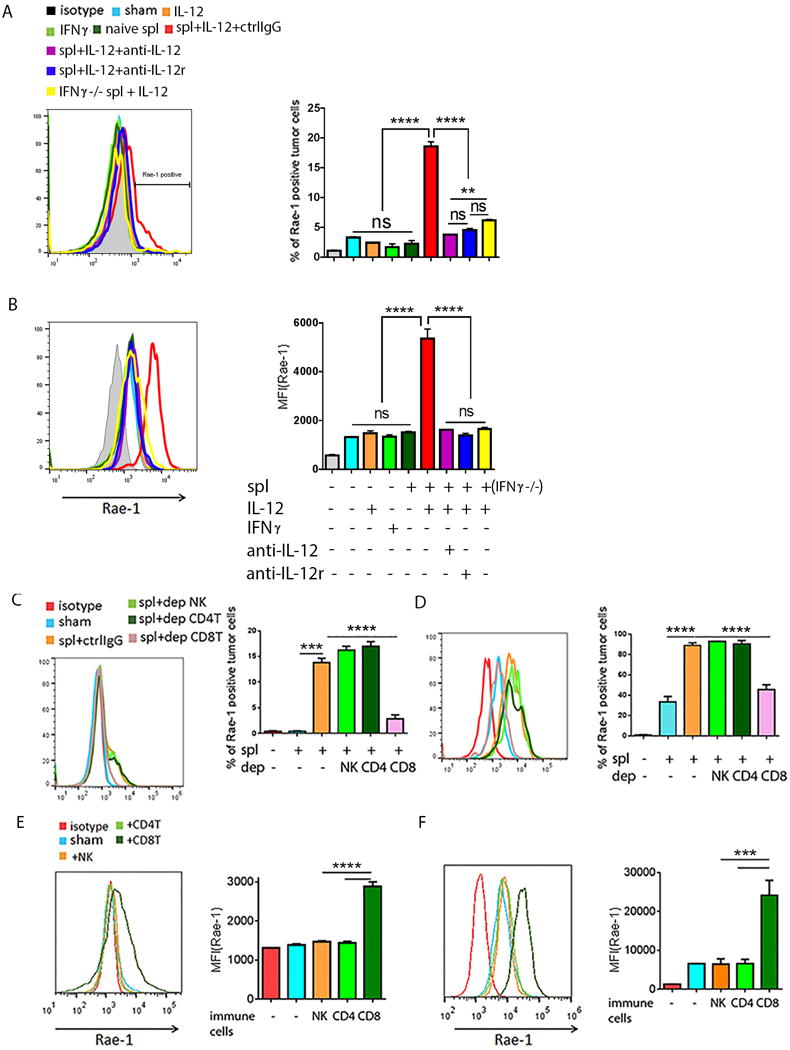
(A, B) Rae-1 on CT26 (A) or K7M3 (B) tumor cells after treated with IL12 (10 ng/ml) or IFNγ (10 ng/ml) recombination protein, or co-incubation with naïve splenocytes or stimulated spl. (C, D) Rae-1 on CT26 tumor cells (C) and K7M3 tumor cells (D) after co-incubation with activated splenocytes lacking the indicated lymphocyte subpopulation through antibody depletion. spl+ctrlIgG: splenocytes plus control IgG; spl+dep NK: splenocytes in which NK cells were depleted; spl+dep CD4T: splenocytes in which the CD4+ T cells were depleted; spl+dep CD8T: splenocytes in which CD8+ T cells were depleted. (E, F) Rae-1 on CT26 (E) and K7M3 (F) tumor cell surfaces after incubation with splenocytes enriched in immune cell subpopulations from wild-type mice as indicated. Bar graphs show percentage of Rae-1+ cells or mean fluorescence intensity (MFI) of Rae-1 as means ± SEM. Results are representative of three repeated experiments.
