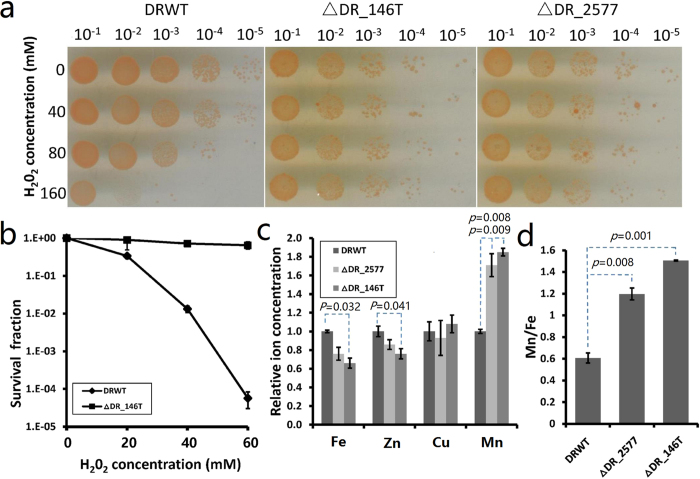
Figure 6. Survival of D. radiodurans wild type and mutant strains exposed to H2O2 treatment.
The ∆DR_146T and ∆DR_2577 showed higher resistance to H2O2 and increased Mn/Fe ratio than D. radiodurans wild type. (a) Comparison of the sensitivity of wild-type (DRWT), ∆DR_146T and ∆DR_2577 strains under H2O2 treatment. Cells (107 CFU ml−1) were dripped onto TGY plates following H2O2 treatment for 30 min and dilution with sterile phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.4). Different dilutions of cell cultures are indicated in the figure. (b) Survival assays of D. radiodurans wild type and ∆DR_146T strains. Cells were suspended in phosphate buffer (107 CFU ml−1), treated with H2O2 for 30 min, and the survival fraction was measured by counting bacterial colonies of treated compared with the untreated samples (0 mM H2O2). (c) ICP-MS analysis of the relative metal ion (Fe, Zn, Cu, Mn) content in wild type and mutant strains. (d) Ratio of Mn and Fe ion content in wild type and mutant strains. Experiments were independently performed three times. P-values indicate the significance compared with wild type cells.