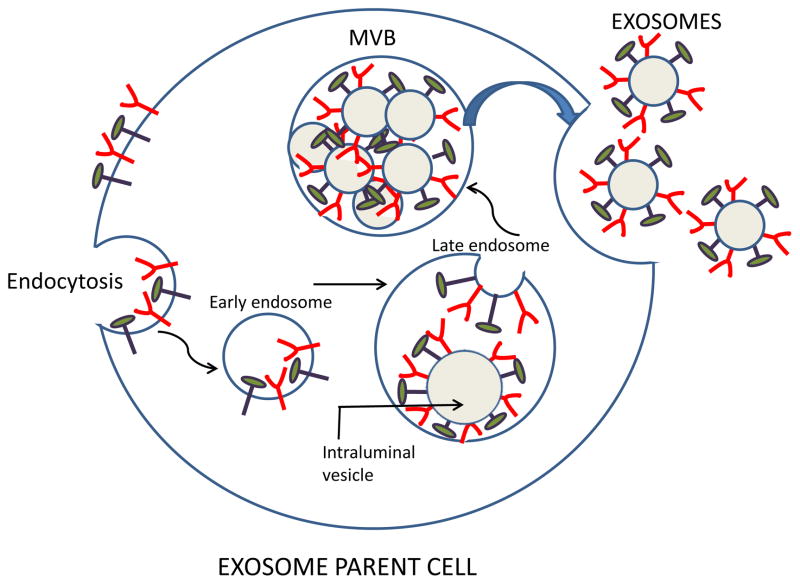
Figure 1.
Exosome biogenesis and their release from a parent cell. The surface membrane undergoes endocytosis enclosing surface-residing molecules into an early endosome. Invagination of the endosomal membrane in late endosomes leads to the formation of intraluminal vesicles, each decorated with molecules originally present on the cell surface. Endosomes form a multivesicular body (MVB) containing pools of intraluminal vesicles. Fusion of the MVB with the cell surface membrane leads to release of free exosomes into the extracellular space. Note that components of the parent cell surface are now present on the membrane surrounding each exosome.