Figure 2.
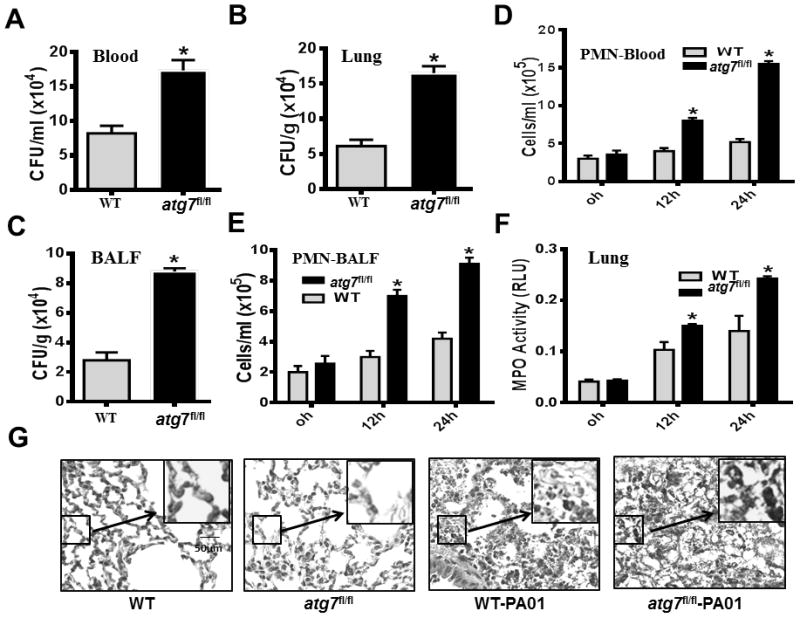
Disruption of Atg7 leads to severe bacterial dissemination, PMN penetration and oxidative lung injury in P. aeruginosa-induced sepsis. (A–C) Twenty-four hours after the onset of i.p. PAO1, blood, lung tissues and bronchoalveolar lavage fluid (BALF) of WT mice and atg7fl/fl mice were collected to detect bacterial dissemination by CFU assay. (*P<0.05; n=5, T tests.) (D–E) At 0, 12 and 24 hours after i.p. injection of PAO1, PMN infiltration levels in the blood and BALF were measured by Hema staining. (*P<0.05; n=5, T tests.) (F) MPO activity in lungs following i.p. PAO1 challenge in WT mice and atg7fl/fl mice. At 0, 12 and 24 hours after i.p. infection with PAO1, lung tissues were collected to determine MPO activity. (*P<0.05; n=5, T tests.) (G) Representative histological views of lungs of WT mice and atg7fl/fl mice after 24 hour i.p. infection with PAO1 by H&E staining (Inset shows the enlarged view). Data are shown as mean ± SEM of three independent experiments (*P<0.05; n=3 mice; T tests.)
