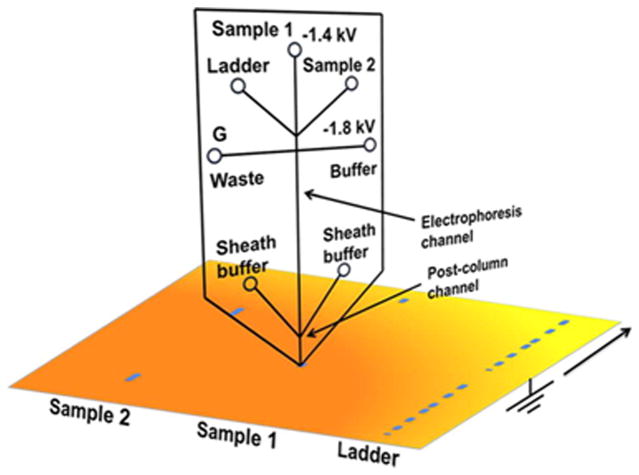
Figure 3.
Protein separation using microchip gel electrophoresis coupled with direct blotting onto a PVDF membrane. The microchip was fabricated with a 2 cm long, 15 μm deep, and 50 μm wide electrophoresis channel and reservoirs for sample, size ladder, buffer, waste, and sheath buffer. Sample and ladder standards were injected into the electrophoresis channel by floating the buffer and waste reservoirs and applying the desired voltage between the sample and grounded membrane support. As in the capillary design, a sheath flow was required to stabilize current. The post-column sheath channel was slightly wider (90 μm) than the separation channel and extends 300 μm. As before, emerging proteins were directly blotted onto a PVDF membrane translated below the sheath channel. (Reprinted with permission from ref. 42. Copyright 2013 American Chemical Society.)