Figure 4.
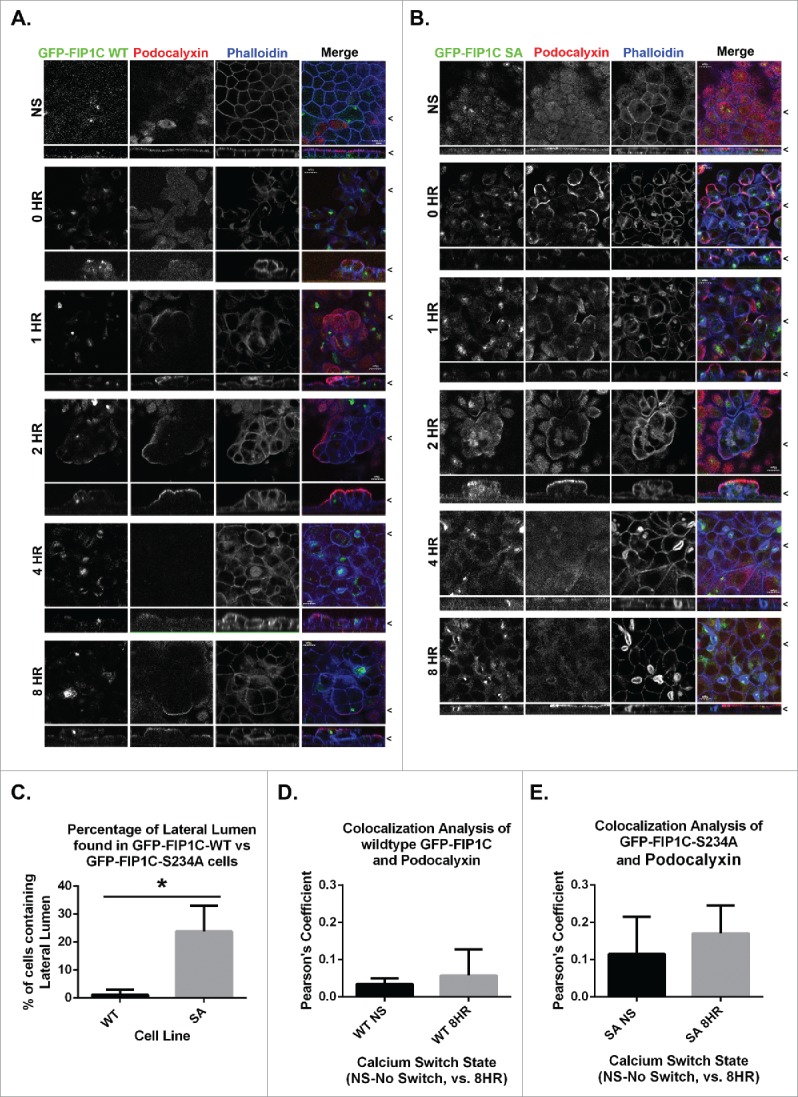
Overexpression of GFP-Rab11-FIP1C wildtype and GFP-Rab11-FIP1C(S234A) causes two distinct phenotypes during calcium switch: pseudo-stratification and lateral lumen formation. MDCK cell lines stably expressing either GFP-Rab11-FIP1C wildtype (A) or GFP-Rab11-FIP1C(S234A) (B) were examined in the non-switched (NS) condition and 0,1, 2, 4, and 8 hours after calcium re-addition with immunostaining with antibody against Podocalyxin along with fluorescent-Phalloidin to visualize F-actin. Overexpression of GFP-Rab11-FIP1C wildtype protein caused a dramatic pseudo-stratification 2 hours into a calcium switch assay. Podocalyxin localized only to the most apical surface of these pseudo-stratified layers. The expression of the GFP-Rab11-FIP1C(S234A) mutant caused some cell stratification, but also induced F-actin accumulation at the lateral membrane greater than 4 hours after calcium switch in lateral lumens. Podocalyxin also lined the lateral lumens. The lateral lumens are seen in WT overexpression lines (see A. 4 HR), however, to a much lesser extent. X/Z images are shown below X/Y images, < indicates where images were taken for X/Y and X/Z planes. All scale bars = 10µm. C. Quantitation of lateral lumen formation. Wildtype GFP-FIP1C overexpression caused lateral lumens to form in ∼1% of cells, whereas, overexpression of FIP1C(S234A) causes lateral lumen to form in ∼25% of cells following calcium switch (*p = 0.00006, error bars represent standard deviation). Colocalization analysis of wildtype GFP-FIP1C (D) and GFP-FIP1C(S234A) with Podocalyxin colocalization demonstrated little colocalization. Graphs plot mean Pearson's Coefficient, error bars represent standard deviation, WT p = 0.17, SA p = 0.19.
