Fig. 3. EGCG selectively inhibits phosphorylation of TAK1 at the Thr184/187 site to inhibit its kinase activity. (A).
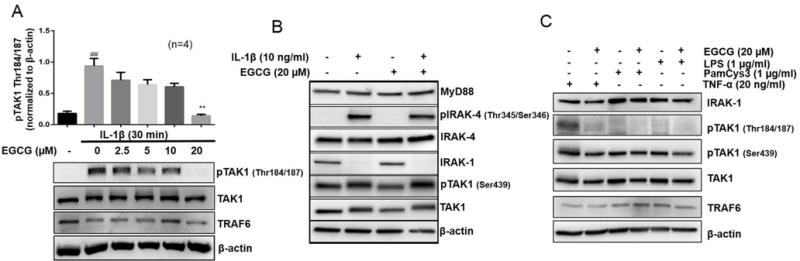
RA-FLS were pretreated with EGCG (2.5–20 μM), followed by IL-1β stimulation for 30 minutes. Cell lysates were analyzed for pTAK1 (Thr184/187), TAK1, TRAF6, and β-actin. (B) RA-FLS treated with IL-1β and/or EGCG (20 μM) were analyzed for MyD88, p-IRAK-4 (Thr345/Ser346), IRAK-4, IRAK-1, pTAK1 (Ser439), total TAK1, or β-actin to validate the selectivity of EGCG for pTAK1 (Thr 184/187). (C) RA-FLS were pretreated with EGCG (20 μM), TLR2 agonist (PamCys3, 1 μg/ml), or TLR4 agonist (lipopolysaccharide, LPS; 1 μg/ml), followed by stimulation with TNF-α (20 ng/ml) for 30 minutes. Cell lysates were analyzed for the expression of IRAK-1, TRAF6, pTAK1 (Thr184/187), pTAK1 (Ser439), total TAK1, and β-actin. The results in each subfigure represents the experiments repeated on four RA-FLS from different donors. ## p<0.01 for NS vs IL-1β; **p<0.01 for IL-1β vs IL-1β+ EGCG.
