Fig. 5.
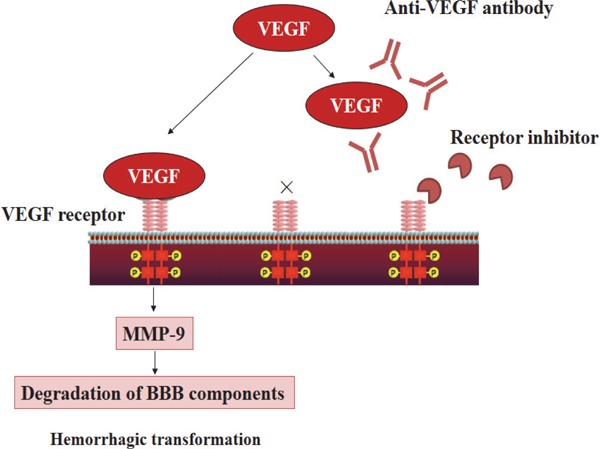
VEGF signaling cascade and anti-VEGF therapy (quoted from reference 57)
After cerebral ischemia, vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) is expressed in the microvascular wall, and receptors that are conjugated to VEGF as a ligand are phosphorylated and activated. The subsequent activation of matrix metalloproteinase-9 (MMP-9) and degradation of protein components of the basal lamina cause intracerebral hemorrhage. The VEGF signaling cascade is inhibited by the anti-VEGF antibody that neutralizes VEGF and VEGF receptor inhibitors that inhibit VEGF receptors from being phosphorylated. BBB, blood-brain barrier.
