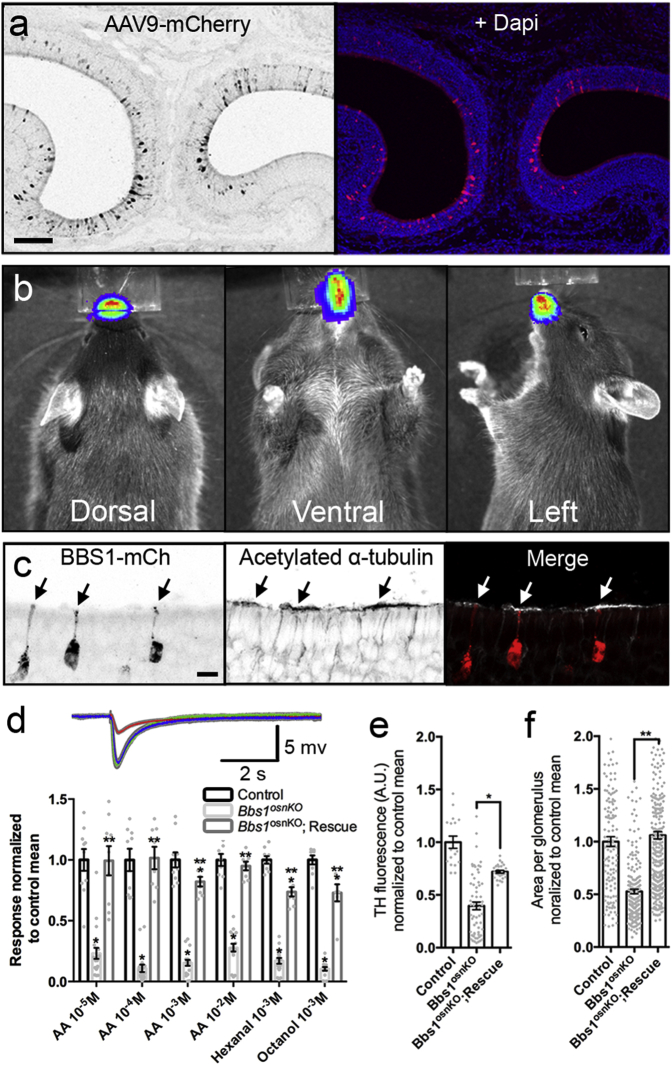
Figure 7.
AAV9-Mediated Rescue of Ciliation and Odor Detection in Bbs1osnKO Mutants
(A) Representative confocal image showing a fixed coronal OE section from a control animal 6 days after AVV9-mediated mCherry delivery. (B) Representative in vivo images showing restriction of infection to the nasal cavity of a control animal 14 days after AAV9-mediated luciferase delivery. (C) AAV9-BBS1-mCherry restores OSN ciliary microtubules in Bbs1osnKO animals. The representative image shows a fixed coronal section of OE from a Bbs1osnKO mutant 3 weeks after treatment with AAV9-BBS1-mCherry, immunostained for acetylated α-tubulin. Acetylated α-tubulin signal intensity is locally increased in the immediate proximity of dendritic knobs (arrows) projecting from AAV-transduced OSNs. (D) Top: representative EOG recordings from the OE surface of the control (green), Bbs1osnKO mutant (red), and BBS1:mCherry-treated Bbs1osnKO mutant (blue) in response to 10−3 M amyl acetate. Bottom: quantified EOG data showing normalized responses to varying AA concentrations, hexanal, or octanol. Rescue animals were treated on P7, P8, and P9 and tested on P38. Compared with untreated mutants, AAV9-BBS1-mCherry-treated Bbs1osnKO mutants showed improved odor detection. Student’s t test, * significantly different from control, ** rescue significantly different from mutant, p < 0.05. (E) Quantification of mean TH fluorescence increased in AAV9-BBS1:mCherry-treated compared with untreated Bbs1osnKO mutants. One-way ANOVA, F(2,104) = 16.26, *p < 0.001, Tukey post hoc test. (F) Quantification of mean glomerular area increase in rescued Bbs1osnKO mutants compared with untreated controls. One-way ANOVA, F(2,613) = 30.12, **p < 0.001, Tukey post hoc test. Values represent means ± SEM. Scale bars, 100 μm (A), 10 μm (C), and 5 mV × 5 s (D).