FIGURE 3.
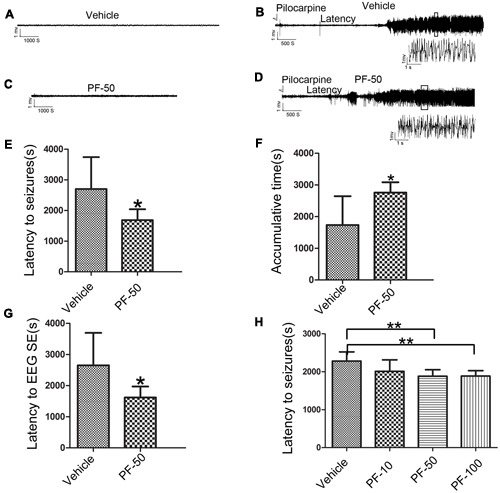
Effect of PF-2545920 on epileptic seizure. (A) Representative figure of LFP under the treatment of vehicle alone. (B) Representative recordings of Licl-Pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus in the vehicle group. (C) Representative figure of LFP under PF-2545920 treatment (50 μM, 10 μL, i.c.v., PF-50). (D) Representative recordings of Licl-Pilocarpine-induced status epilepticus after PF-2545920 administration (50 μM, 10 μL, i.c.v., PF-50). (E) Behavioral evaluation revealed that the latency time in the PF-2545920-treated group was significantly decreased compared with the vehicle-treated group (50 μM, 10 μL, i.c.v., PF-50; n = 8–9, *P < 0.05). (F) Behavioral evaluation demonstrated that the cumulative time of generalized tonic clonic seizures in PF-2545920-treated group increased significantly compared with the vehicle-treated group (50 μM, 10 μL, i.c.v., PF-50; n = 8–9, *P < 0.05). (G) EEG evaluation of latency time to full electrographic SE in PF-2545920-treated group was statistically decreased compared with the vehicle-treated group (50 μM, 10 μL, i.c.v., PF-50; n = 8–9, *P < 0.05). (H) Behavioral evaluation demonstrated that latency time in PF-2545920-treated groups at 50 and 100 μM were statistically decreased compared with the vehicle-treated group (10 μM, 10 μL, PF-10; 50 μM, 10 μL, PF-50; 100 μM, 10 μL, PF-100; n = 7, **P < 0.01).
