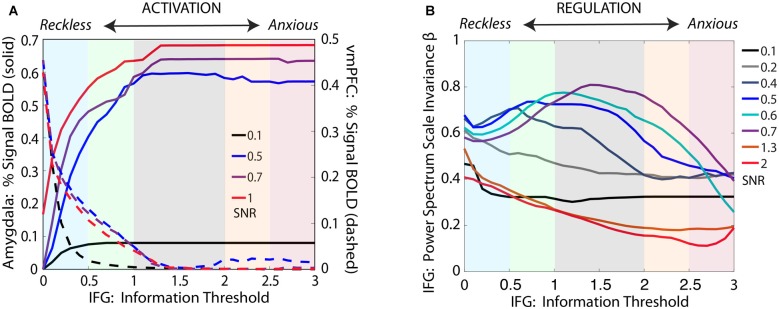
Figure 6.
Simulations for our computational model, shown in Figure 5, cohere with convergent experimental results across the threat-detection spectrum, for threat stimuli at varying levels of signal/noise (SNR). (A) For ambiguous threat, activation for amygdala and vmPFC increase and decrease, respectively, across the reckless to anxious spectrum. (B) The IFG shows pink noise dynamics at the center of the spectrum, with shifts towards white noise dynamics at both ends of the spectrum. Importantly, our simulations demonstrate that the effect is not seen for either very low SNR (0.1–0.2) or very high SNR (1.3–2), but becomes evident only when the brain is challenged with ambiguous data (SNR = 0.05–0.07).