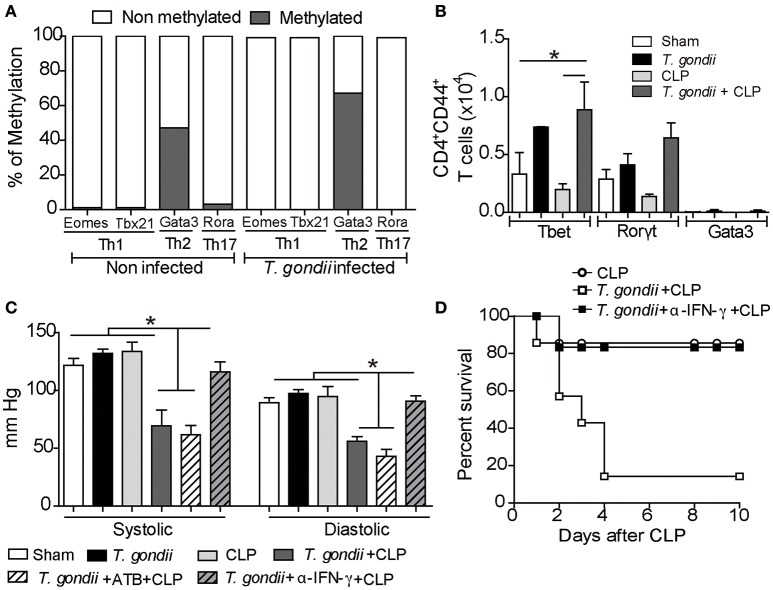
Figure 5.
Treatment with anti-IFN-γ prevents hypotension and ameliorates host survival. For the methylation analysis, CD4+ T cells were separated from spleen cells by negative selection for DNA extraction. The pattern of DNA methylation was determined using the EpiTect Methyl II PCR Arrays kit. This analysis was performed in two independent trials, and the variation rate ≥ 10% was considered significant (A). The expression of the transcription factors T-bet, Gata-3 and RorγT was determined in CD44highCD4+ T cells using flow cytometry (B). For blood pressure analysis, a group of coinfected mice was pretreated with broad-spectrum antibiotics (ATB) 2 weeks before and after T. gondii infection, and another group was treated with anti-IFN-γ antibodies 24 h before CLP induction. After 40 days of T. gondii infection, the mice were subjected to CLP, and at 24 h post-CLP, the blood pressure (mmHg) was evaluated in the animal tail using a sphygmomanometer (C). The bars represent the means ± SEM for 4 animals per group (*p < 0.05). The survival assay was monitored for 10 days after treatment with a 10 μg/kg dose of anti-IFN-γ antibodies (D). The results are expressed as a percentage of survival, and the p-value was considered when comparing chronic T. gondii infected/CLP mice who received antibody treatment vs. animals that were not treated.