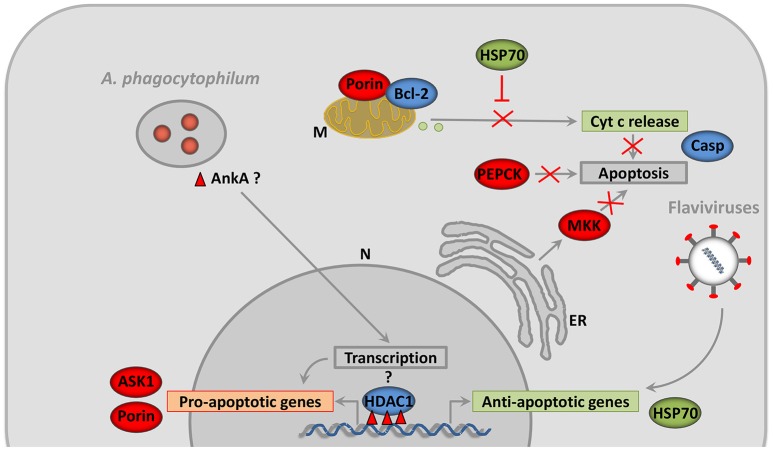
Figure 4.
Pathogens inhibit vector cell apoptosis by different mechanisms. After infection of tick salivary glands, A. phagocytophilum inhibit apoptosis by decreasing the expression of the pro-apoptotic genes coding for proteins such as ASK1 and Porin. Porin down-regulation is associated with the inhibition of mitochondrial Cyt c release (Ayllón et al., 2015a). In contrast, A. phagocytophilum infection does not affect Bcl-2 levels, probably because this protein but not Porin is essential for tick feeding (Ayllón et al., 2015a). A. phagocytophilum also induces ER stress in tick cells which play a role in reducing the levels of MKK that inhibits apoptosis (Villar et al., 2015a). Another interesting mechanism of A. phagocytophilum to inhibit apoptosis is the manipulation of glucose metabolism by reducing the levels of PEPCK (Villar et al., 2015a). The capacity of A. phagocytophilum to downregulate gene expression in neutrophils was associated with HDAC1 recruitment to the promoters of target genes by the ankyrin repeat protein AnkA (Garcia-Garcia et al., 2009a,b; Rennoll-Bankert et al., 2015). Tick HDAC1 is overrepresented in A. phagocytophilum-infected salivary glands and chemical inhibition of this protein decreases A. phagocytophilum burden in tick cells (Cabezas-Cruz et al., 2016). Infection of tick cells with flaviviruses results in the up-regulation of genes such as hsp70 that inhibit apoptosis (Mansfield et al., 2017). N, Nucleus; M, Mitochondria; ER, Endoplasmic Reticulum; Cyt c, Cytochrome c; ASK1, Apoptosis signal-regulating kinase 1; MKK, Mitogen-activated Protein Kinase; HDAC1, Histone Deacetylase 1; AnkA, Ankyrin A; PEPCK, Phosphoenolpyruvate Carboxykinase; FOXO, Forkhead box O; Hid, Head involution defective; JNK, Jun amino-terminal kinases; Casp, caspases. The molecules and processes represented in green are up-regulated, while those represented in red are down-regulated in response to infection. The activity of the molecules represented in blue varies in response to infection.