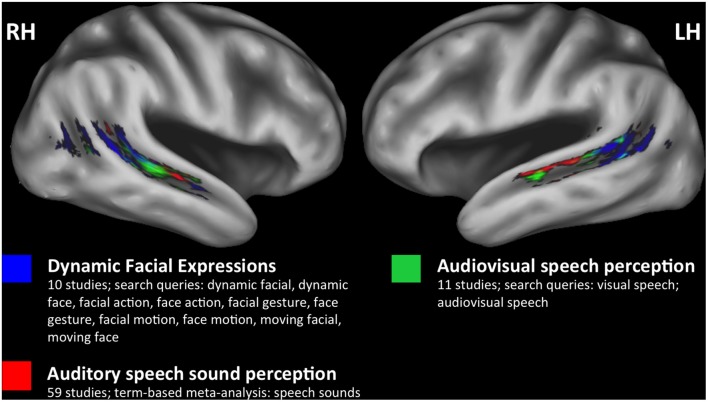
Figure 1.
Meta-analyses. A posterior to anterior gradient of effects related to visual and auditory speech information in bilateral superior temporal sulcus (STS). Three separate meta-analyses were performed using NeuroSynth (http://neurosynth.org) to identify studies that only included healthy participants and reported effects in STS. Two custom meta-analyses (dynamic facial expressions, audiovisual speech) and one term-based meta-analysis (speech sounds) were performed (see color key for details). The FDR-corrected (p < 0.01) reverse inference Z-statistic maps for each meta-analysis were downloaded from NeuroSynth for plotting. Results from dynamic facial expressions (blue), audiovisual speech (green), and speech sounds (red) meta-analyses are plotted on the study-specific template in MNI space (see “Study-Specific Anatomical Template” Section) and restricted to an STS region of interest to highlight the spatial distribution of effects within the STS (see “STS Region of Interest Analysis” Section).