Figure 2.
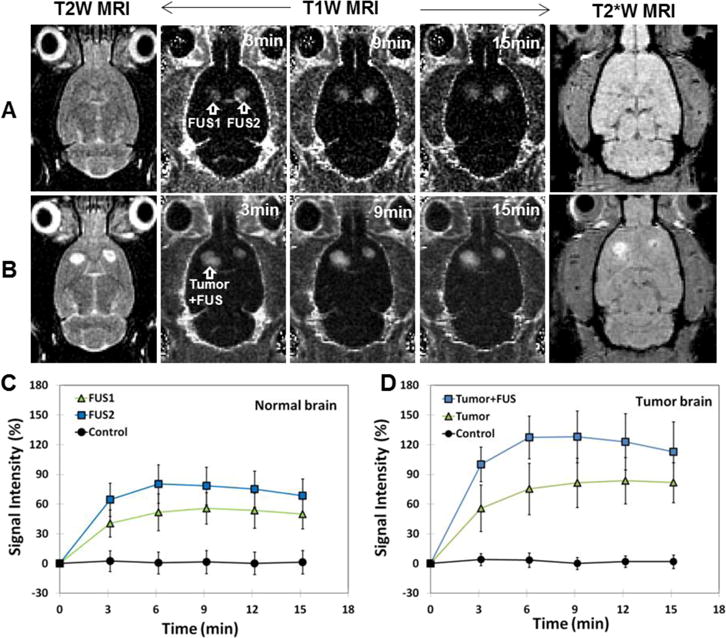
BBB and BTB permeabilization by FUS and microbubbles. A–B. MRI evaluation of FUS-induced BBBD/BTBD and tissue damage in the normal (A) and tumor-bearing (B) rat brain. T2-weighted (T2W) MR images show the tumor locations before sonication. The tumor in one hemisphere was sonicated; the non-sonicated tumor served as a control. T1-weighted (T1W) MR images show contrast changes relative to pre-contrast images. After sonication, a time series of axial contrast-enhanced T1W MR images show localized BBBD at two sonicated spots (arrows) in normal brain (A) and enhanced BTBD at a sonicated region in a brain tumor (B). T2*-weighted (T2*W) MR images in axial plane after FUS showed no evidence of the creation of extensive petechiae, which would have appeared in this imaging as hypointense spots. C: In normal brain, mean signal intensity changes as function of time for 5×5 voxels regions of interest at the two sonicated targets (FUS1 and FUS2) and non-sonicated locations (Control). D. Mean signal intensity changes as function of time for 5×5 voxels regions of interest in the sonicated tumor (Tumor+FUS), the non-sonicated tumor (Tumor), and non-sonicated normal tissue (Control). A PRFP amplitude 0.72 MPa was used to induce BBBD/BTBD. Scale bars are 5 mm.
