Fig. 3.
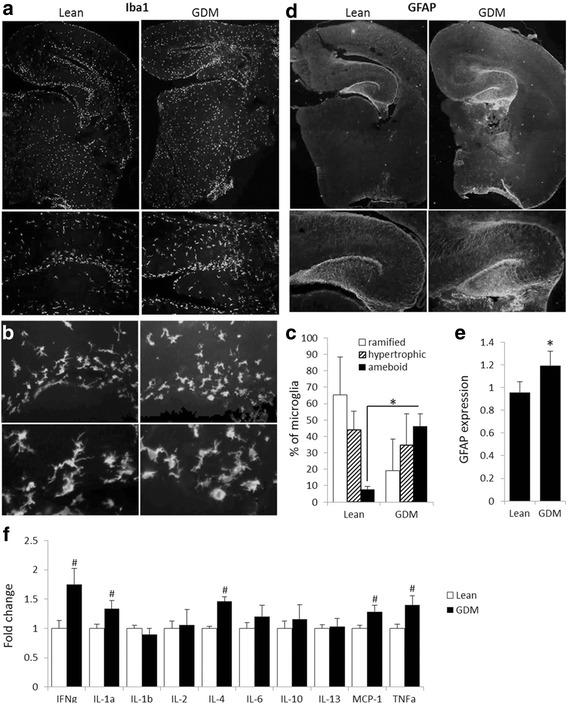
Gestational diabetes mellitus induces neuroinflammation in the offspring brain (at 20E). Micrographs of immunostaining with Iba1 and GFAP demonstrate elevated neuroinflammation status throughout the rat embryo brain. a, b Iba1 allows visualization of microglial morphology. The microglia of embryos from GDM dams have more activated, amoeboid morphology compared to embryos from dams with healthy pregnancy of which majority possess resting, ramified microglial morphology. d Increase in GFAP expression seen in embryos of GDM dams reflects on astroglial activation and chronic inflammation. Quantitative analysis of hippocampal Iba1-positive cells (c) and GFAP staining (e) confirms the elevated neuroinflammation in GDM offspring. f Cytokine analysis demonstrates increase in pro-inflammatory cytokines (IFNγ, TNFα, IL-1, MCP-1), while only IL-4 was elevated from the anti-inflammatory cytokines (IL-4, IL-10, IL-13). *p ≤ 0.05 compared to lean, n = 6
