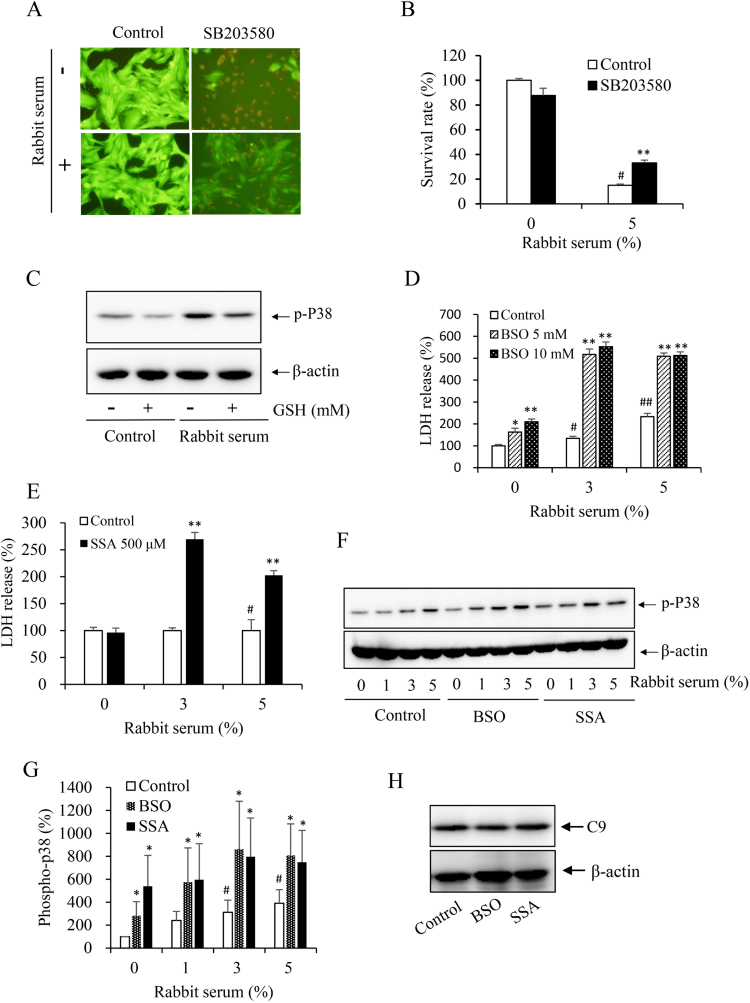
Fig. 6.
Mediating role of p38 in complement-elicited cell death and its inhibition by GSH. (A, B) Effect of P38 in antibody/complement-initiated cell death. MCs preloaded with calcein-AM were exposed to 5% rabbit serum in the presence or absence of p38 inhibitor SB203580 (10 μM) for 6 h. Note the reduced number of PI-positive dead cells in SB203580-treated cells. The intensity of green fluorescence was determined with a fluorescence reader at 490–515 nm. The rate of cell survival relative to untreated control was calculated (Fig. 6B). # P<0.01 vs. control; ** P<0.01 vs. 5% rabbit serum control. (C) Induction of p38 phosphorylation by the rabbit serum and its prevention by GSH. MCs were incubated with 1% rabbit serum in the presence or absence of 2.5 mM GSH. The cellular lysates were subject to Western blot analysis of the level of phospho-p38. β-actin was used as loading control. (D-G) Depletion of intracellular GSH on antibody/complement-induced cell death and P38 activation. MCs were pretreated with the indicated concentration of BSO (D), or 500 μM SSA (E) for 6 h before exposing to rabbit serum for an additional 6 h. (F) MCs were pretreated with 10 mM BSO or 500 μM SSA before exposing to the indicated concentrations of rabbit serum for 15 min. The cellular lysates were subject to Western blot analysis of the level of phospho-p38. (G) Densitometric measurement of band intensity in F. Data shown are mean ±SE (n =4). # P<0.05 vs. zero control; * P<0.05 vs. respective control. H. Effect of GSH-modulating chemicals on cellular deposition of C9. Cells were pretreated with 5 mM BSO and 500 μM SSA for 6 h, followed by reaction with 10 μg/ml Thy-1 plus 10% native human serum for an additional 1 h. The cellular lysates were subjected to Western blot analysis of C9.