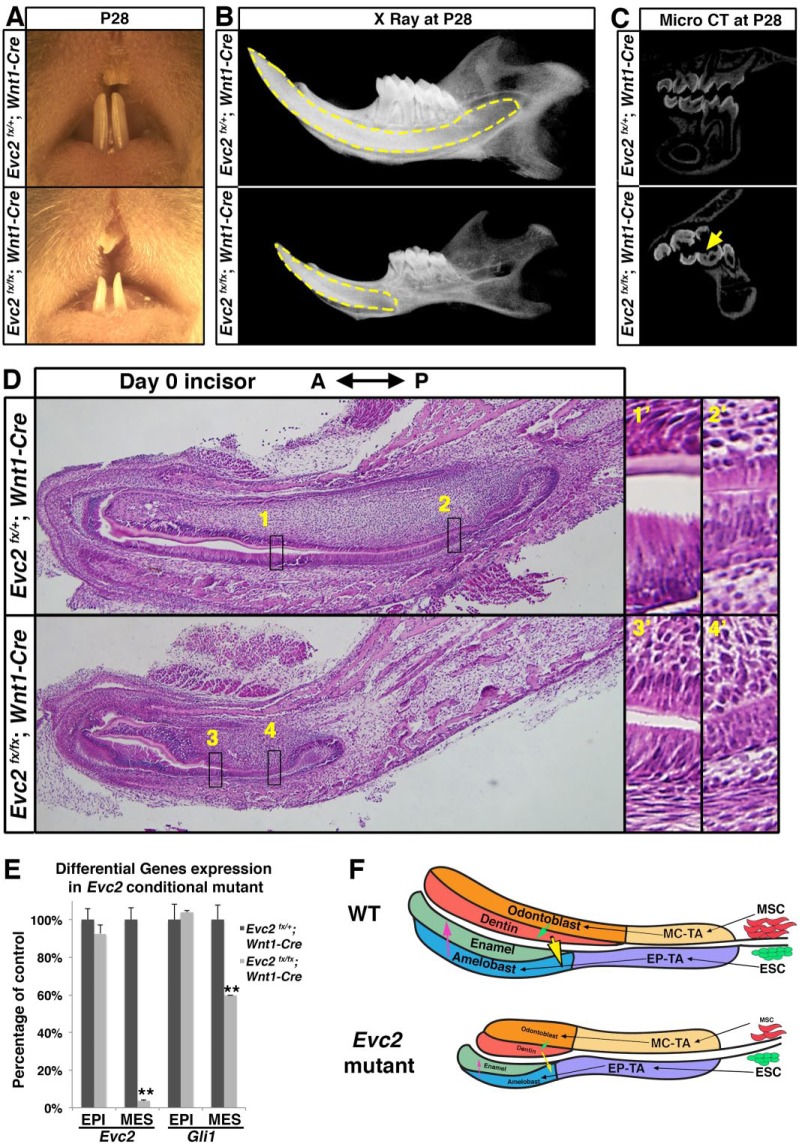
Figure 5.
Mesenchyme-specific deletion of Evc2 phenocopied hypomorphic tooth formation found in Evc2 global knockout incisors. (A) Frontal view of maxilla and mandible incisor of Evc2 conditional knockout mice at postnatal day 28 (P28). (B) X-ray radiogram of Evc2 conditional mutants showed hypomorphic tooth formation. Mandibles of Evc2 conditional mutants and littermate controls at P28 were dissected and sagittal X-ray radiography was performed. Yellow dashed lines indicate incisors. (C) Micro–computed tomography (CT) of Evc2 conditional mutants and littermate controls at P28 indicates hypomorphic enamel in molars. (D) Mandible incisors of mesenchyme-specific Evc2 mutants and littermate controls were sagittally sectioned and processed for hematoxylin and eosin staining. Regions in boxes in both control and mutant were enlarged and shown on the right. (E) Quantitative reverse transcribed polymerase chain reaction from incisor epithelium and mesenchyme indicated that Wnt1-Cre–mediated deletion of Evc2 is specific for dental mesenchyme. EPI and MES stand for epithelial and mesenchymal tissues, respectively. n = 3, **P < 0.001. (F) A model to explain how mesenchymal function of Evc2 secondarily affects enamel formation. EP-TA, epithelial transient amplifying cells; ESC, dental epithelial stem cells; MC-TA, mesenchymal transient amplifying cells; MSC, dental mesenchymal stem cells. See text for details.