Figure 2.
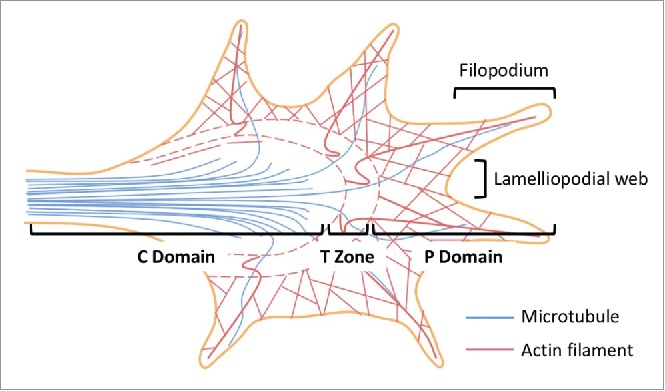
Axonal growth cone structure. Three functionally distinct regions have been identified in the growth cone - the central (C) and the peripheral (P) domains, as well as the transitional (T) zone. The C domain is at the end of the axonal shaft where the microtubules extending from the axonal shaft terminate. The C domain are also rich in numerous organelles including mitochondria and exocytotic vesicles. The primary function of the C domain is to support the P domain, which consists primarily of actin cytoskeleton and has a dynamic morphology. In between the C and the P domains lies the T zone where microtubules interact with actin filaments through acto-myosin contractile structures. Filopodia-like finger protrusions at the P domain are supported by the lamellipodia-like web structures. This figure is adapted from Box 1 in Ref. 4.
