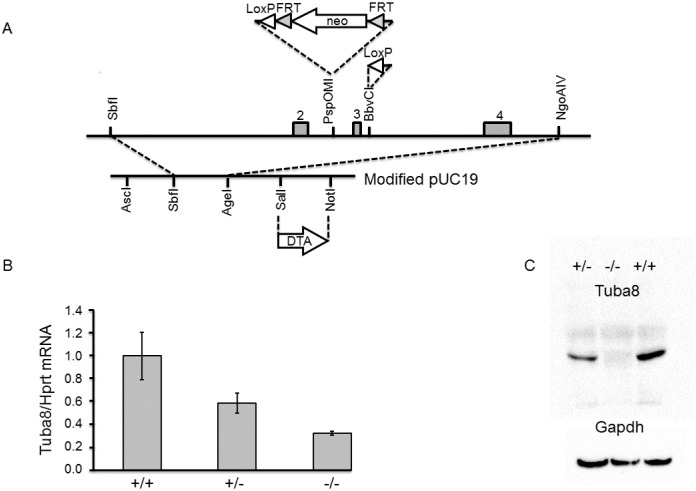
Fig 1. Generation of a Tuba8 knockout allele.
A) Design of the targeting construct. A 9.1-kb SbfI–NgoAIV genomic fragment was directionally cloned into the SbfI+AgeI-restricted pUC19 vector. The shaded numbered boxes depict exons 2–4. The arrows represent the location and direction of expression of the selectable markers. The neomycin (neo) cassette, obtained from PGKneobpA [22], was inserted at the PspoMI site. The FRT sites (shaded arrow heads) flanked the neomycin positive selection cassette, whilst one LoxP site flanked one side of the neo, and the second was inserted into the BbvCI site in intron 3 (unshaded arrow heads). The diphtheria toxin negative selection cassette, PGK-DTA (kindly provided by P. Soriano, Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center, Seattle, WA), was inserted between the SalI and NotI sites of the modified pUC19 backbone. B) Quantitative reverse transcription PCR. Tuba8 mRNA levels in testis were determined from four animals of each Tuba8 genotype, wild type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−) and homozygous (−/−), and normalised to Hprt levels. Bars indicate mean ± 1 s.d. Statistical significance was reached for all combinations of genotypes using an unpaired t-test (p<0.05). C) Protein analysis using western blotting. Protein lysates from testis samples used four animals of each genotype: wild type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−) and homozygous (−/−), in lanes 1–3 respectively, were probed with the Bioserv Tuba8 mouse monoclonal antibody. A band of approximately 55 kDa was detected in the wild type and heterozygous samples. The blots were subsequently probed for Gapdh expression as a loading control to quantify expression.